Comparing Aluminum Brazing Furnace and Crucible Melting
Explore key differences between aluminum brazing furnaces and crucibles for melting aluminum.
| Features | aluminum brazing furnace | cruciblefor aluminum melting |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Control | Precise temperature and atmosphere control | Manual heat control, no atmosphere regulation |
| Purpose | Joins aluminum with strong, clean brazed joints | Holds and melts aluminum simply |
| Output Quality | Produces uniform, high-strength joints | Quality depends on operator skill |
| Design Complexity | Complex system with sensors and chambers | Simple pot made from heat-resistant materials |
| Production Scale | Ideal for large-scale, continuous production | Best suited for small batches or hobby use |
| Energy Efficiency | Energy-saving with advanced heating methods | Less efficient, more heat loss |
| Safety Features | Built-in safety controls and closed chamber | Requires careful manual handling and PPE |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance costs | Low cost and affordable for beginners |
| Maintenance | Regular sensor and chamber upkeep needed | Simple cleaning and crack checks required |
| Portability | Large, fixed industrial equipment | Small, easy to move and set up |
For aluminum melting, many people think the aluminum brazing furnace works better. It gives more control over heat and keeps the quality steady. This way is good for people who want the same results every time and need to melt a lot of aluminum. Some people pick a crucible because it is cheaper and simpler to use. It is best for small jobs. Using an aluminum brazing furnace can make things safer and the quality better. A crucible is better for fast and easy melting jobs.
Key Takeaways
- Aluminum brazing furnaces give exact heat control. They melt aluminum in a cleaner way. This makes them good for big jobs. They are also best for high-quality aluminum products.
- Crucibles are easy to use and not expensive. You can move them around easily. They work best for small jobs. Beginners and hobbyists like them. They help when you need to melt aluminum fast and simply.
- A brazing furnace lowers oxidation and mistakes. It does this by using nitrogen or a vacuum. This helps make the metal stronger. It also makes the metal look better.
- Crucibles need careful use and safety gear. They can be risky for workers. There is a higher chance of burns. There is also a risk of contamination.
- Induction furnaces heat aluminum fast and evenly. They save energy. They make better quality metal than gas-fired furnaces.
- Picking a furnace or crucible depends on your job size. It also depends on your budget and the quality you want. Big factories usually use furnaces. Small shops often pick crucibles.
- Brazing furnaces need regular care to work well. You must check sensors and chambers often. Crucibles need to be checked for cracks and damage a lot.
- DAG says aluminum brazing furnaces are best for steady and safe melting in factories. They also save energy. Crucibles are better for small, cheap, and flexible jobs.
Quick Comparison
Table Overview
| Aspect | Aluminum Brazing Furnace | Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Makes and controls heat with exact temperature and air settings | Holds melted aluminum, stands up to heat and chemicals |
| Purpose | Gives a controlled space for strong, clean joints | Holds melted aluminum and keeps it clean |
| Output Quality Impact | Gives even, clean, and strong brazed joints | Keeps melted aluminum steady and pure |
| Design & Materials | Has a complex setup with a heating area, insulation, and controls | Simple container made from materials that resist heat |
| Role in Process | Controls brazing for top results | Keeps aluminum steady while it melts |
Note: The table shows an aluminum brazing furnace manages melting. A crucible just holds and protects the melted aluminum.
Key Differences
- Aluminum brazing furnaces have advanced control systems. These systems use thermocouples or infrared sensors. They keep the aluminum at the right temperature.
- Crucibles do not control the melting environment. They only hold the aluminum as it melts. Most crucibles are made of graphite or ceramic. These materials handle high heat and stop chemical reactions.
- Aluminum brazing furnaces often use nitrogen or vacuum. This stops oxidation and keeps the melted aluminum clean.
- Crucibles can be used in different furnaces. Some are induction or gas-fired. Induction furnaces heat aluminum fast and evenly. They also save energy and lower oxidation.
- Aluminum brazing furnaces are good for big jobs. They melt and braze large amounts of aluminum with steady quality. Crucibles are best for small batches or hobbies. They are easy to move and cost less.
- Safety features are different. Aluminum brazing furnaces have cooling, overcurrent protection, and interlocks. Crucibles depend on the furnace’s safety and need careful handling to avoid spills or burns.
Tip: Use an aluminum brazing furnace for steady, high-quality results with lots of aluminum. Use a crucible for simple, small melting jobs.
Aluminum Brazing Furnace
How It Works
An aluminum brazing furnace uses controlled heat to join or melt aluminum parts. First, workers clean the aluminum pieces to get rid of dirt and oxide. Then, they put the parts together with filler metal at the joint. The furnace heats everything in a special chamber. This chamber uses a vacuum or nitrogen gas to stop oxidation. The temperature goes up until the filler metal melts. The base aluminum does not melt. The melted filler flows into the joint by capillary action. Afterward, the furnace cools the parts down. Workers clean off any leftover flux. This method keeps the aluminum clean and makes strong joints.
Main steps in aluminum brazing furnace operation:
- Clean the aluminum parts to remove oxides and contaminants.
- Put the parts together with the filler metal in place.
- Place the assembly inside the furnace chamber.
- Heat the assembly in a vacuum or with protective gas.
- Let the filler metal melt and flow into the joint.
- Cool the assembly after brazing.
- Clean off any extra flux from the finished part.
Note: The aluminum brazing furnace keeps things safe and steady. It uses exact temperature control and a clean space.
Pros
Efficiency
An aluminum brazing furnace works well for melting lots of aluminum. It can handle many parts at the same time. The furnace uses advanced controls to keep the heat steady. This saves energy and melts aluminum faster. Big batches move through the furnace quickly. This is good for factories that need to melt or braze a lot of aluminum.
Temperature Control
Temperature control is a big advantage. The furnace uses sensors and computers to keep the heat just right. This stops the base aluminum from melting while the filler flows. Every part gets even heating. Barcode systems can match each batch to a program. This makes the process repeatable and easy to track.
Quality
The aluminum brazing furnace makes strong, clean joints. The vacuum or gas stops oxidation and keeps the aluminum pure. This means fewer defects like pinholes or weak spots. The process also keeps the parts from changing shape. The joints resist rust and look smooth. These features make the furnace great for high-quality aluminum products.
Cons
Cost
The aluminum brazing furnace costs more than simple crucibles. The price is higher because of the advanced controls and special chambers. Factories also pay for regular maintenance and skilled workers.
Complexity
This furnace has a complex design. Workers must follow careful steps for cleaning and assembly. The process needs tight fits between parts for the filler to flow well. Planning and setup take more time than basic melting.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is needed for safe and steady work. The furnace must be cleaned to remove flux and build-up. Sensors and controls need checking often. If the furnace uses a vacuum or gas, those systems need care too. These jobs add to the time and cost of using the furnace.
Tip: The aluminum brazing furnace gives better control and quality. But it needs more money and careful work.
Use Cases
The aluminum brazing furnace is best for places needing top quality. Factories use it to make car radiators and oil coolers. They also use it for heat exchangers. These things need strong and clean joints. The furnace gives even heat and a safe place for aluminum. This helps stop oxidation and keeps the metal pure.
Main Industrial Applications
- Car part factories use the furnace for radiators and air conditioners.
- Appliance makers use it for heat exchangers and condensers.
- Aerospace and electronics companies use vacuum brazing for small parts.
- Construction and new energy plants use it for big jobs.
Note: The aluminum brazing furnace works for both big and small jobs.
Advanced Features Comparison
| Feature Aspect | Continuous Aluminum Brazing Furnace | Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Has automatic controls for steady heating | Has automatic controls for exact heat and cooling |
| Protective Atmosphere | Uses nitrogen and hydrogen to stop oxidation | Works in a vacuum to stop oxidation without flux |
| Energy Efficiency | Saves energy by using less and wasting less | Very efficient because it does not use flux |
| Production Suitability | Good for making lots of the same thing fast | Makes fewer parts but with higher quality |
| Customization & Automation | Can change size and settings; has smart controls and automation | Made for special parts; has automatic temperature control |
| User Operation | Easy controls make it simple to use and fix | Automated process means less work for people |
DAG’s aluminum brazing furnace is special because it gives steady heat. It uses nitrogen or a vacuum to protect the metal. This makes it better than simple holding furnaces for clean, strong joints. The furnace saves energy and can be set up for different sizes and speeds.
Why Choose This Furnace?
Many companies use the aluminum brazing furnace for big jobs. It keeps the heat steady and stops cracks or weak spots. The vacuum type does not need flux, so parts are cleaner and need less cleaning. Automation lets workers do more in less time. It also keeps the quality the same for every batch.
Tip: If a factory needs to melt and join a lot of aluminum with high quality, the aluminum brazing furnace works better than basic tools.
Crucible for Aluminum Melting

How It Works
A crucible is a strong pot that holds aluminum. Heat from a furnace melts the aluminum inside. The furnace can use charcoal, gas, or electricity as fuel. Here are the steps for melting aluminum with a crucible: 1. Put on safety gear and get all your tools ready. 2. Start the furnace by lighting it or turning it on. 3. Place the crucible inside when the furnace is hot. 4. Add more fuel around the crucible and close the lid. 5. Drop small pieces of aluminum into the crucible. 6. Wait for the aluminum to melt and add more if needed. 7. Watch as the aluminum turns from solid to liquid. 8. Use a tool to skim off the dross on top. 9. Add flux and degassing agents to make the metal better. 10. If needed, let in more air to make it hotter. 11. Use tongs to pick up the crucible and pour the melted aluminum into molds. 12. Let the metal cool down and get hard.
Note: The crucible must handle very high heat and keep the aluminum clean while it melts.
Pros
Simplicity
Crucible melting is easy to set up and use. People do not need much training to start. There are no tricky controls or fancy systems. Most people can learn how to melt aluminum this way fast. Maintenance is simple, so the equipment does not break often.
Affordability
Crucibles cost less than big furnaces. You do not need much money to buy one. This makes them good for small shops or people who do metalwork as a hobby. They use less energy and do not need many repairs. You can treat the melted aluminum right in the crucible, so you need fewer tools.
Portability
Crucible systems are small and easy to move. You can set them up in different places. This helps if you need to melt small amounts or work in new spots. It is quick to get started and easy to move the equipment.
Tip: Crucible melting is great for small jobs, quick changes, and custom work.
Cons
Control
Crucible melting does not give much control over heat or air. People must watch the temperature closely. If the heat is not even, the crucible or aluminum can get damaged. There are no special sensors or automatic controls.
Contamination
Crucibles can add dirt or other things to the aluminum. Graphite crucibles can break down and add carbon to the metal. Alumina crucibles do not react much but cost more and heat up slower. Using a crucible a lot can cause flakes or scales that get into the aluminum.
Safety
Crucible melting can be risky. High heat can hurt the crucible if you go over the limit. Not using safety gear or handling things wrong can cause burns or accidents. Always check the crucible for cracks or damage before using it. Checking often helps stop accidents and keeps everyone safe.
| Drawback/Risk | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Temperature Limitations | Using the crucible too hot can make it crack or melt. |
| Material Degradation | Flaking and breaking down can make the crucible not last long and dirty the metal. |
| Capacity Constraints | Small crucibles cannot melt a lot of aluminum at once. |
| Energy Inefficiency | Some heat escapes, so melting can waste energy. |
| Frequent Replacement | Crucibles wear out and need to be replaced often. |
Note: Always wear safety gear and check your tools before melting aluminum.
Use Cases
Crucibles are used in many ways for melting aluminum. People pick them for different jobs and setups. The type, size, and material of the crucible change how melting works and what you get in the end.
Types of Crucibles and Their Suitability
| Crucible Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Good heat transfer, low cost, easy to handle | Can oxidize, less durable in harsh conditions |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Strong, resists corrosion, lasts longer | Can react with aluminum, higher price, lower shock resistance |
| Ceramic (Alumina) | High purity, handles high heat, does not react with aluminum | Brittle, cracks with fast temperature changes, more expensive |
Graphite crucibles are picked for fast melting and low price. Silicon carbide is chosen when you need something tough. Ceramic crucibles are best if you want pure metal, but they can break easily.
Common Applications
- Hobbyists melt scrap aluminum at home with crucibles. They use small amounts and simple tools.
- Small shops use crucibles for custom casting or fixing things. They need to set up fast and change jobs quickly.
- Mobile setups use crucibles to melt aluminum in different places. Workers can move the tools where they need them.
- People use crucibles for testing new alloys or shapes. Small batches help save metal and cut waste.
Crucibles are good for small jobs, quick changes, and moving around. They are not right for big factories that need lots of metal and perfect quality.
Importance of Matching Crucible to Furnace
- The crucible must handle the furnace’s highest heat and not react with aluminum.
- The crucible’s size and shape must fit inside the furnace. If not, it can waste energy or cause spills.
- Induction furnaces need crucibles with the right electrical features. The wrong one can get too hot or not work well.
- The crucible should hold enough aluminum for the job. There must be space to stir and for the metal to grow when hot.
- If you pick the wrong match, it can make the metal dirty, waste energy, or break the furnace.
Always follow the furnace maker’s tips when picking a crucible. The right choice keeps things safe and the metal clean.
Aluminum Melting Furnace Types
There are different kinds of aluminum melting furnaces. Each kind heats aluminum in its own way. Some are better for certain jobs than others. The main types are induction, gas-fired, and electric furnaces. Picking the right furnace depends on how much aluminum you need to melt. It also depends on the quality you want and how much money you can spend.
Induction
An induction furnace heats aluminum with electromagnetic fields. This way, the metal gets hot fast and evenly. Induction furnaces use energy well, up to 90%. They let you control the temperature very closely. You can set the heat just right. This helps make melted aluminum that is the same every time and has fewer bad spots.
Induction furnaces work for both small and big batches. They start and stop quickly, so you can change jobs fast. These furnaces do not have open flames, so there is less oxidation. This makes the area safer and cleaner. Induction furnaces cost more at first and need skilled workers. But they save energy and make better aluminum in the long run.
Tip: Induction furnaces are good for factories that want top-quality aluminum and lower energy bills.
Gas-Fired
Gas-fired furnaces use natural gas or other fuels to heat aluminum. They cost less to set up than electric furnaces. Many foundries pick gas-fired furnaces because they are cheaper at first. But these furnaces lose more heat when running. Their energy use is not as good, only about 20% to 50%.
It is harder to control the temperature in gas-fired furnaces. The heat can go up and down, which causes more oxidation. This means you lose more metal and the quality is not as high. Gas-fired furnaces also make exhaust gases. These can hurt the environment and need extra safety steps. Gas-fired furnaces are best for melting a lot of aluminum when you need to save money. But they do not make the best quality aluminum.
| Furnace Type | Energy Efficiency | Temperature Control | Product Quality | Safety | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Induction | High | Excellent | High | Very Good | High-quality, flexible jobs |
| Gas-Fired | Medium-Low | Moderate | Medium-Low | Moderate | Large, budget-focused jobs |
| Electric | High | Good | High | Very Good | Clean, efficient operations |
Electric
Electric furnaces melt aluminum using resistance or arc heating. They turn electricity into heat to melt the metal. Electric furnaces heat up fast and let you control the temperature well. They do not make flames or exhaust gases, so they are safer and cleaner.
Electric furnaces use less energy than gas-fired ones. Some induction electric furnaces use about half the energy of gas-fired types. Advanced controls keep the heat steady, so the melted aluminum is better. Small electric furnaces are good for small shops. Big ones work for large factories. Electric furnaces cost more to buy, but they save money on energy and repairs over time.
Note: Electric furnaces help companies make aluminum in a cleaner way and lower pollution.
Aluminum Melting: Key Factors
Volume
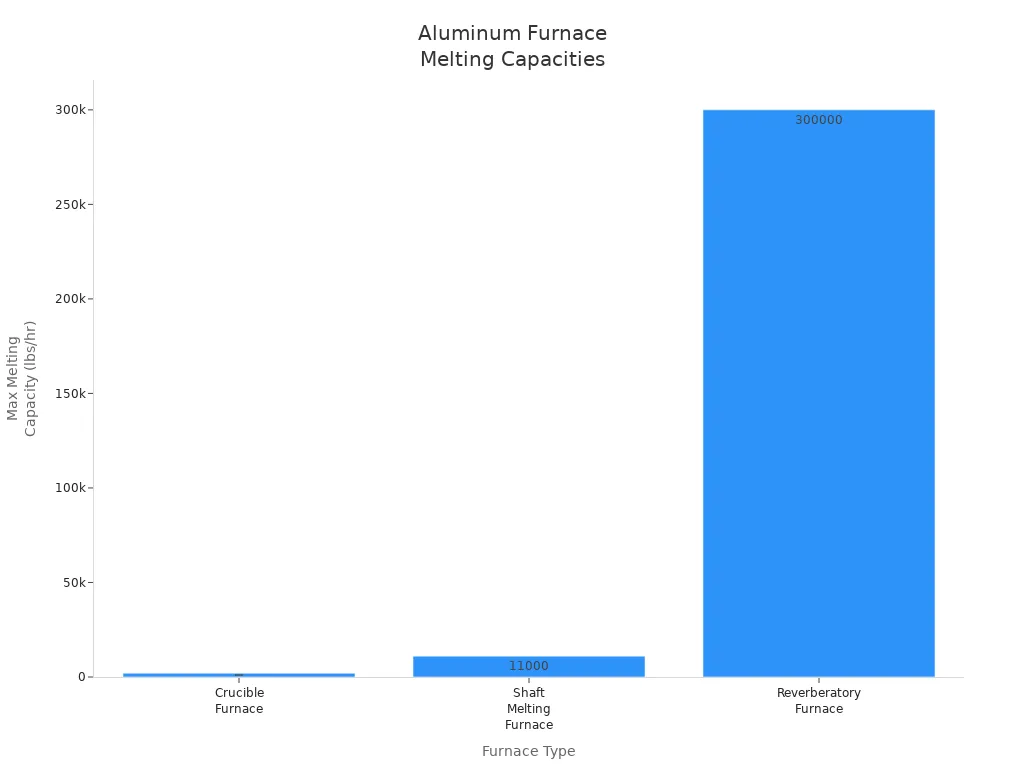
How much aluminum you need to melt is important. Crucible furnaces are best for small jobs. They can melt up to about 2,000 pounds each hour. This works well for small shops or people who need to change what they melt often. Big furnaces like reverberatory or shaft types can melt much more. Reverberatory furnaces hold from 3,000 to 300,000 pounds. These are used in big factories for melting lots of aluminum at once. Shaft melting furnaces are in the middle. They can melt about 11,000 pounds per hour and use fuel well.
You need to pick the right crucible size for your job. If the crucible is too small, it slows things down. If it is too big, it wastes energy. How you put aluminum in, how well the crucible handles heat changes, and the power you have also matter.
| Furnace Type | Suitable Melting Volume Range | Key Characteristics Relevant to Volume and Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible Furnaces | Small volumes, flexible melting rates | Up to ~2,000 lbs/hr aluminum; quick alloy changes; small footprint |
| Reverberatory Furnaces | Large bulk melting and holding | 3,000–300,000 lbs capacity; best for single alloy; variable efficiency |
| Shaft Melting Furnaces | Medium to large volumes | ~11,000 lbs/hr; efficient fuel use; melt on demand; automation possible |
Tip: Use a crucible furnace for small jobs or if you change alloys a lot. For big jobs, pick a reverberatory or shaft furnace.
Quality
Quality is another thing to think about. Good aluminum needs to stay clean and not get too much air. A little bit of oxygen helps stop gas from getting in. Taking out hydrogen is important because it can make the metal weak. You must keep the temperature just right. If it gets too hot, the aluminum can get ruined.
Vacuum brazing furnaces make strong and clean joints. They use special systems to control heat and air. This makes them good for jobs where the joints must be perfect. Crucibles are easy to use but do not give as much control. How you pour the aluminum also changes how the metal turns out.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Advanced systems in brazing furnaces ensure precise melting conditions |
| Atmosphere Control | Nitrogen or vacuum reduces oxidation and contamination |
| Pouring Technique | Careful pouring minimizes gas pickup and agitation |
| Degassing | Dry nitrogen helps prevent gas defects |
Note: If you want the best aluminum, use a brazing furnace with good controls. For simple casting or small jobs, a crucible can work.
Budget
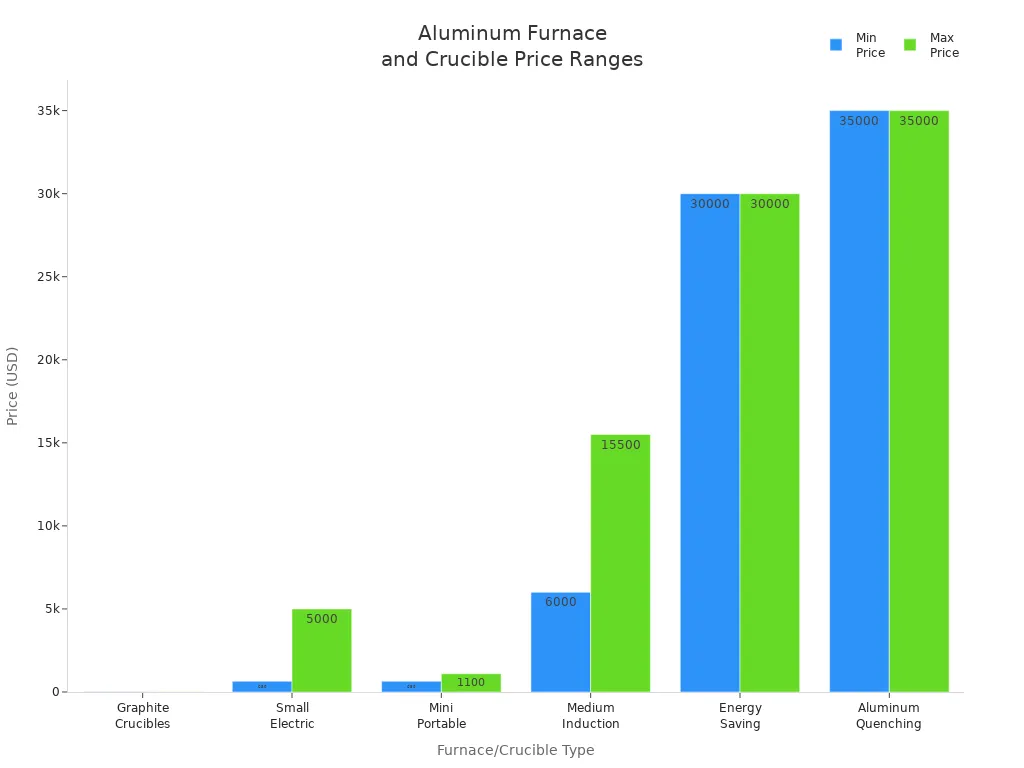
How much money you have is a big part of picking equipment. Crucibles start at about $15, so they are cheap for small shops or hobbyists. Small electric crucible furnaces cost from $650 to $5,000. Mini induction furnaces cost $650 to $1,100. Medium induction furnaces cost $6,000 to $15,500. Big industrial furnaces can cost $30,000 or more. The largest ones can be about $35,000.
You need to think about how much you can spend and what you need. Big furnaces cost more to buy and fix, so plan carefully. Cheap crucibles save money but may not work for big jobs or high quality.
| Furnace/Crucible Type | Price Range (USD) | Notes on Impact on Selection Process |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite Crucibles for Aluminum Melting | Starting around $15 | Very low cost, good for small jobs. |
| Small Electric Crucible Furnaces | $650 – $5,000 | Suitable for small-scale operations. |
| Mini Portable Induction Crucible Furnaces | $650 – $1,100 | Good for precise, small batch melting. |
| Medium Induction Crucible Melting Furnaces | $6,000 – $15,500 | Higher capacity and precision, higher cost. |
| Energy Saving Pressure Casting Holding Crucible Furnaces | Around $30,000 | High-end, energy-efficient, for large-scale production. |
| Aluminum Quenching Furnace with Crucible Smelting Pot | Around $35,000 | Large industrial scale, significant investment. |
Note: Always look at both the first price and the cost to run the furnace before you buy.
Safety
Safety is very important when picking between an aluminum brazing furnace and a crucible for melting aluminum. Each way has its own dangers and safety rules.
Crucible Safety Considerations:
- Crucibles must be made from strong materials like alumina ceramic, graphite, or steel. These can take the high heat needed to melt aluminum.
- Workers should wear heat-resistant gloves or use tongs. These tools help stop burns and accidents when moving hot crucibles.
- Good airflow is needed. Melting aluminum makes fumes like aluminum oxide. Breathing these fumes can hurt your lungs.
- Fire safety is important. Molten aluminum can catch fire if it touches water or things that burn. Fire extinguishers should be close by to stop fires fast.
- Wearing safety gear is a must. Gloves, goggles, and long sleeves keep you safe from splashes of hot metal.
Aluminum Brazing Furnace Safety Considerations:
- These furnaces use exact temperature controls and different heating zones. This keeps the heat steady and helps stop overheating.
- Controlling the air inside is important. Many furnaces use a vacuum or special gas to stop oxidation. This keeps the area safer and the metal cleaner.
- The furnace is built to be safe. The closed chamber and automatic controls help prevent accidents.
- Workers still need to wear safety gear. Even with more machines, gloves and goggles protect from rare splashes or leaks.
Tip: Both ways need careful work and the right safety gear. Aluminum brazing furnaces have more built-in safety features. Crucibles need workers to pay more attention.
Here is a table to compare the main safety points:
| Safety Aspect | Aluminum Brazing Furnace | Crucible for Aluminum Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Control | Automatic, steady | Manual, can change quickly |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum or inert gas, less oxidation | Open air, more oxidation risk |
| Protective Gear | Needed, but less direct handling | Needed, more direct handling |
| Fire Risk | Lower, closed system | Higher, open system |
| Fume Exposure | Lower, controlled environment | Higher, needs good ventilation |
Note: The best method depends on what safety is needed for the job. Factories often use aluminum brazing furnaces for safer, big jobs. Small shops or hobbyists may use crucibles but must follow all safety rules.
Choosing the Right Method
For Beginners
If you are new, you want something easy and safe. You also want it to be cheap. Crucible melting is a great pick for people just starting out. It uses simple tools and does not need special skills. Most beginners can use a crucible with just basic safety gear and a small furnace. You can watch the aluminum melt and control the process. This helps you learn faster.
When looking at ways to join aluminum, being easy to use is very important for beginners. MIG welding is liked because it is quick and does not cost much. It feeds wire by itself and works well for thick aluminum. TIG welding gives more control but is harder to learn. Stick welding is easy to move but makes rougher work and needs more cleaning.
| Method | Beginner Suitability | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible | High | Simple, low cost, portable |
| MIG Welding | High | Fast, easy to learn |
| TIG Welding | Low | Needs skill, slower |
| Stick Welding | Low | Messy, less control |
Tip: If you are new, try a crucible or MIG welding first. These ways help you build skills and feel sure before using harder tools.
For Small Business
Small businesses want to save money but still get good results. Crucible melting is good for small jobs and custom work. If a business grows, it might use modular induction furnaces or buy melted aluminum from others. Buying melted aluminum means you do not need to buy big machines. It also saves money on fixing and running equipment.
Now, many companies sell furnaces that use less energy and have smart features. These furnaces help small businesses spend less on workers and power. Modular designs let a company add more furnaces as they get more orders. Automatic controls, like remote use and data tracking, make work safer and faster.
- Buying melted aluminum saves money at the start and lets you focus on your main work.
- Modular induction furnaces melt aluminum fast, make less pollution, and are easy to add more.
- Automatic systems mean you need fewer workers and make things safer.
Note: Small businesses should look at all costs, like energy and workers, before picking a way to melt aluminum. Modular and automatic systems are often best when you need to make more products.
For Industry
Big factories need ways to melt lots of aluminum and keep the quality the same. Gas-fired and reverberatory furnaces are used most in big factories. These furnaces can melt a lot at once and do not cost too much. They burn fuel, which is good for melting all day.
Some factories use induction or cold crucible furnaces for special metals or when they need very clean aluminum. Induction furnaces let you control the heat very well and use less energy, but they are better for smaller jobs. Cold crucible furnaces stop dirt from getting in and use vacuum or special gas, so they are good for special uses.
- Gas-fired and reverberatory furnaces are best for melting a lot of aluminum for less money.
- Induction furnaces are good for small or special jobs that need exact heat.
- Cold crucible furnaces keep the metal pure for special alloys.
Big factories should pick the furnace that fits how much they need to melt and the quality they want. For most big jobs, gas-fired or reverberatory furnaces are the best mix of size and cost.
DAG Recommendations
When you pick between an aluminum brazing furnace and a crucible, think about what you need most. Each way works best for different people and jobs. The table below shows which one is good for each user:
| User Type | Best Method | Why It Works Best |
|---|---|---|
| Hobbyist | Crucible | Simple, low cost, easy to move |
| Small Business | Crucible or Small Furnace | Flexible, affordable, quick setup |
| Large Industry | Aluminum Brazing Furnace | High quality, large volume, steady results |
DAG says to use an aluminum brazing furnace if you want the best and same results every time. This furnace lets you control the heat very well. It uses nitrogen or vacuum to keep the aluminum clean. Factories that make car parts or radiators get the best results with this furnace. It can melt many pieces at once. It also saves energy and keeps workers safe.
If you have a small shop or just like to try things, a crucible is a good choice. It costs less and is easy to set up. You can melt a little aluminum and change what you do fast. You do not need much training to use a crucible. It is good for people who want to learn or work in new places.
DAG’s aluminum brazing furnace is special because it has smart controls for heat. It uses gas or vacuum to stop the aluminum from getting dirty. You can change the furnace to fit different jobs. This helps factories make what they need. The furnace also uses less energy, so it saves money over time.
Note: DAG says to pick the way that matches your job, how good you want the metal, and how much you can spend. For big jobs and the best results, use an aluminum brazing furnace. For small jobs or learning, a crucible is enough.
DAG also helps people who want to start using a furnace instead of a crucible. They help with setting up, teaching, and fixing the furnace. This makes it easier and safer to switch.
Key things to remember:
- Use a crucible for small and easy jobs.
- Pick an aluminum brazing furnace for big jobs and top quality.
- DAG furnaces give better control, safety, and save energy.
- DAG can help you get better tools as your work grows.
If you follow these tips, you can choose the best way for your work. This helps you do a better job and save money over time.
Industry studies say the best way to melt aluminum depends on how much you need and how good you want it. Aluminum brazing furnaces let you control heat better. They are good for big jobs or when you want top quality. Crucibles are great for small amounts or if you are learning. The table below shows the main points:
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Induction or brazing furnace |
| Cost | Crucible for small jobs |
| Scale | Furnace for industry, crucible for hobby |
You should pick your aluminum melting way based on what you need, how much money you have, and how safe it is. If you want to know more, check out guides about picking furnaces and getting materials ready.
FAQ
What makes an aluminum brazing furnace better for large-scale melting?
An aluminum brazing furnace keeps the heat just right. It can melt lots of aluminum without stopping. This is best for factories that need to melt or join a lot of aluminum and want the same results every time.
Can a crucible melt the same amount of aluminum as a brazing furnace?
A crucible cannot melt as much aluminum as a brazing furnace. Crucibles are good for small jobs or hobbies. Big jobs need a furnace to work faster and safer.
Which method gives better quality aluminum?
An aluminum brazing furnace makes cleaner and stronger joints. It uses special air inside to stop the metal from getting dirty. Crucibles can let in dirt if you do not use them carefully.
Is a crucible easier to use than a brazing furnace?
Yes, a crucible is easier to set up and use. Most people can learn to melt aluminum with a crucible fast. A brazing furnace takes more training and careful steps.
Which option costs less for beginners?
A crucible costs much less than a brazing furnace. People who are new or have small shops usually pick crucibles because they do not cost much.
How do safety features compare between the two methods?
A brazing furnace has safety controls and a closed box. This helps stop accidents. Crucible melting needs you to be careful and wear more safety gear.
Can both methods work for different aluminum alloys?
Both ways can melt different aluminum alloys. But a brazing furnace lets you control the heat and air better. This helps keep the alloy good.
What maintenance does each method require?
A crucible needs you to check for cracks and clean it after each use. A brazing furnace needs regular checks for its sensors, chambers, and gas parts to keep it safe and working well.