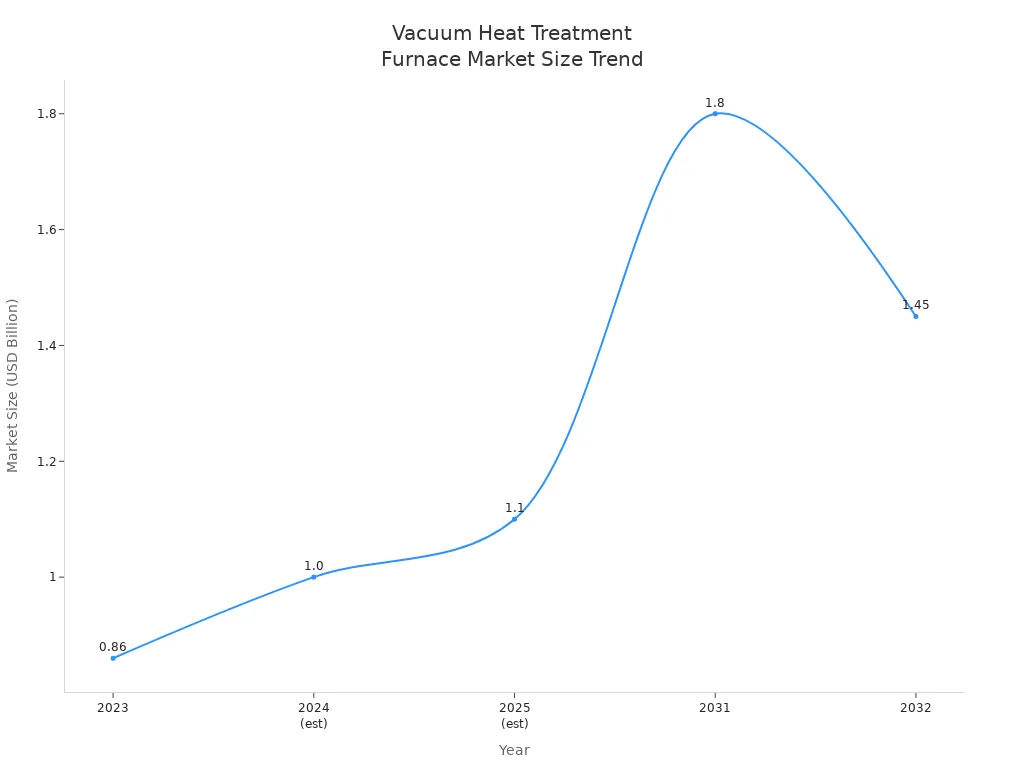
A vacuum heat treatment furnace works with metals in a vacuum. This helps make the metal better. The furnace takes away oxygen. This stops oxidation and keeps the metal clean during heat treatment. The vacuum gives even heating and cooling. This makes the surfaces cleaner and the parts stronger. The process helps make good products for cars and electronics. The world market for vacuum heat treatment furnaces may reach about USD 1.1 billion in 2025. This shows the market is growing.
A radiator brazing furnace uses this method. It helps make heat exchangers that work well every time.
Key Takeaways
- Vacuum heat treatment furnaces make metal better by taking out air. This stops oxidation and helps heat the metal evenly. These furnaces use strong stuff like graphite and molybdenum. They can handle very high heat, up to 2200°C, without problems. The vacuum keeps metal surfaces clean and lowers the chance of mistakes. It also makes parts stronger and more dependable.
- Vacuum heat treatment uses less energy than old methods. It also makes less pollution and helps things get made faster. There are different furnace types for different jobs. Single-chamber, multi-chamber, and continuous furnaces help meet many needs and goals. Some special vacuum furnaces, like the DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace, give exact control.
- They help make really good aluminum parts. Vacuum heat treatment is very important in many industries. It is used in aerospace, cars, electronics, medical tools, and new energy. It helps make safe and long-lasting parts. To get good results, you must load the furnace right. You also need to control the temperature and keep the vacuum working well. This helps the furnace last longer and work better.
Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnace
Definition
A vacuum heat treatment furnace is a special machine. It does heat treatment in a vacuum. The furnace has a sealed chamber. This chamber takes out air and gases. It makes a low-pressure space. The vacuum heat treatment furnace can do quenching, annealing, tempering, and brazing. It keeps metal surfaces clean and shiny. Manufacturers use vacuum furnaces for metals and ceramics. These are used in cars, planes, electronics, and medical tools.
Key technical features for a vacuum heat treatment furnace in 2025 are:
- Furnace chambers use graphite or molybdenum. These are strong and seal well.
- Heating elements are graphite or molybdenum. They can get as hot as 1350°C.
- Vacuum pumps include rotary vane, diffusion, and turbomolecular pumps. They reach vacuum levels as low as 7×10⁻¹ Pa.
- PLC-based systems control the temperature.
- Inert gas or oil quenching systems cool things quickly.
- Water cooling systems protect the furnace shell and vacuum pump.
- Loading systems help move materials safely and easily.
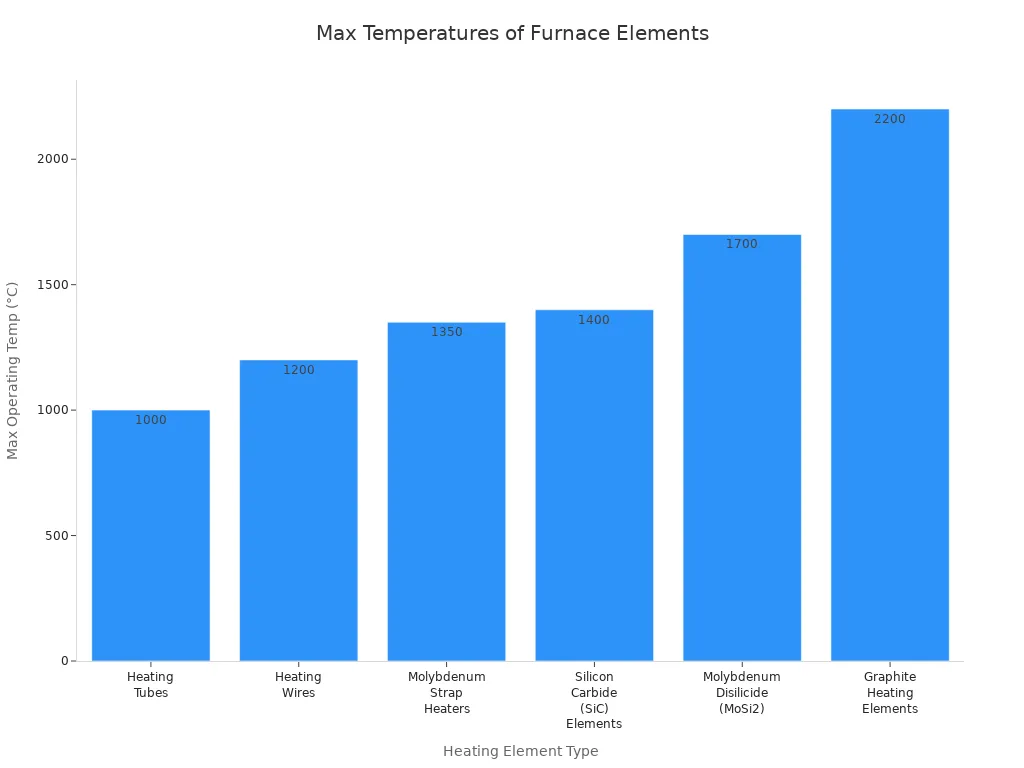
| Heating Element Type | Maximum Operating Temperature | Typical Applications / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Tubes | 1000°C | Used for low-temperature jobs like annealing or brazing |
| Heating Wires | 1200°C | Good for sintering ceramics and other moderate heat jobs |
| Molybdenum Strap Heaters | 1350°C | Used for treating tough metals at high temperatures |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements | 1400°C | Used for advanced ceramics or glass work |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | 1700°C | Used for pure jobs like making semiconductors |
| Graphite Heating Elements | 2200°C | Used for very hot jobs, like carbon composite sintering |
Working Principle
The vacuum heat treatment furnace works by sealing the workpiece inside. It removes air to make a vacuum. Pumps and valves lower the pressure a lot. Sometimes, it goes below 1.33×10⁻³ Pa. Electric heating elements, like graphite rods or molybdenum wires, make heat. They use electrical resistance. The temperature control system manages how fast it heats and cools. This helps treat the material just right.
The vacuum lets the furnace do many jobs:
- Quenching, tempering, and sintering metals
- Annealing and brazing parts
- Making high-grade steels and electronic materials
- Making car and industrial parts
The vacuum heat treatment process takes away gases and organic stuff from the metal. This gives a bright, clean finish and better strength. The vacuum furnace can do carburizing, nitriding, and degassing. The clean environment gives good, repeatable results.
Why Vacuum?
The vacuum is important for good heat treatment. Taking out air, especially oxygen and nitrogen, stops oxidation and contamination. This keeps the metal surface clean. The sealed chamber keeps out dust and dirt.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Stops heat loss by convection and stops oxidation. |
| Oxygen-Free Chamber | Stops chemical reactions with air. This is important for brazing and sensitive materials. |
| Enclosed Design | Keeps samples safe from dust and smoke. |
Heating in a vacuum furnace removes dirt and oxide layers. The vacuum heat treatment process keeps things clean. This is important for sensitive materials and special uses. No air means you can control chemical reactions and surfaces well. This gives better product quality and longer life for parts.
Tip: Vacuum heat treatment furnaces help makers get clean surfaces and strong parts. This is why they are used in important industries.
Advantages of Vacuum Heat Treatment
Material Quality
Vacuum heat treatment makes materials better in many ways. The process takes out oxygen and other gases from the chamber. This stops oxidation and decarburization. Metals keep their smooth and clean surfaces. The treatment keeps each part strong and looking good. Heating is even, so every batch is the same. This helps companies make products people can trust.
- Vacuum heat treatment stops oxidation and decarburization. This gives cleaner and smoother surfaces.
- The process heats everything evenly. All parts get the same material properties.
- Even heating and cooling stop stress and bending. This makes materials stronger and last longer.
- Better uniformity means parts work well, even in tough jobs like cars and planes.
- The vacuum keeps out dirt and stops oxidation. This makes materials higher quality and more reliable.
- Good temperature control and special heat settings help get the best results.
- These changes help materials last longer and save money over time.
Vacuum heat treatment keeps metals pure and strong. Companies use this method for important parts.
Clean Processing
Vacuum heat treatment makes a cleaner place to work than old furnaces. The vacuum chamber keeps waste gases and liquids inside. This keeps the air and workplace clean. Vacuum furnaces use electric pumps, not burners. This lowers pollution and saves energy.
- The vacuum blocks outside dirt. This lets oxidizing agents break down and makes the vacuum cleaner.
- Closed vacuum furnaces give better control and are better for the planet. They lower pollution and keep things safe.
- Vacuum designs stop dirt and deep oxidation. These problems happen in old furnaces.
- There is no oil or flame smoke, so the workplace is safer and cleaner.
- The process removes gases and bad stuff from metal surfaces.
- Lowering the vacuum pressure breaks down oxide layers. This keeps surfaces clean.
- This way works well for metals that rust easily. It keeps their strength.
Vacuum heat treatment helps make things in a green way. It helps companies follow rules and keep workers safe.
Process Control
Vacuum heat treatment lets people control every step closely. Special control systems let workers set up and watch the process in real time. This makes sure every batch gets the same treatment.
- Gas quenching or pressure systems control the air. This helps make the heat cycle just right and lowers mistakes.
- Even heating comes from putting parts in the right spot and using good heat plans and tools.
- Controlled heating and cooling stop bending and help keep sizes right.
- These controls help make sure parts are strong and the right size. This is important for making things in factories.
Vacuum heat treatment is about keeping things clean and controlled with the right temperature. Features like special heat exchange and many heating zones give steady and even heat. New vacuum furnaces heat and cool fast and do it the same way every time. This is great for companies that need the same quality every time.
Keeping the right temperature in vacuum heat treatment furnaces is very important. Chillers help keep the furnace cool and steady. This stops changes that can mess up the process. A steady temperature means every batch is treated the same. Steady heat also stops problems and keeps the furnace safe, helping companies make good products.
Note: Vacuum heat treatment lets companies get the same, high-quality results every time. This control is very important for jobs that need things to be just right.
Comparison with Conventional Methods
Vacuum heat treatment is different from old heat treatment ways. These differences change how much energy is used and how fast things get done. They also change how good the products are and how safe the workplace is.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Vacuum heat treatment uses much less energy than old furnaces. People who run these furnaces save about half their energy. The process is also faster. It can finish jobs up to 40% quicker. This helps companies do more work in less time.
- Vacuum heat treatment cuts energy use by half.
- It needs much less gas, using up to 99% less.
- CO2 emissions go down by as much as 89%.
- The furnace heats and cools fast, so it works well.
Product Quality and Metallurgical Benefits
Vacuum heat treatment lets people control the process better. The vacuum stops oxidation and decarburization. This keeps metal surfaces clean and strong. Even heating lowers stress in the metal. Parts bend less—up to 70% less than with salt bath treatment. This means more parts pass quality checks.
| Feature | Vacuum Heat Treatment | Conventional Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Low (up to 50% less) | High |
| Cycle Time | Shorter (up to 40% less) | Longer |
| Gas Consumption | Minimal | High |
| CO2 Emissions | Low | High |
| Surface Quality | Clean, bright | Often oxidized |
| Deformation | Minimal | More common |
| Safety | No open flames | Open flames, more hazards |
| Automation | High | Lower |
Safety and Environmental Impact
Vacuum heat treatment does not use open flames. This makes it safer for workers. The closed system keeps pollution out of the air. Companies can use these furnaces with machines that work by themselves. This helps make more products and keeps the air cleaner.
Note: Vacuum heat treatment makes better products and helps keep workers safe. It is also better for the planet.
Vacuum heat treatment has many clear benefits over old ways. It saves energy, works faster, and makes cleaner, stronger parts. It also helps make the workplace safer and more efficient.
Vacuum Furnace Components

Chamber
The chamber is the main part of a vacuum furnace. It must handle very high heat and pressure. Makers use strong materials like molybdenum and graphite. Molybdenum does not melt easily and does not change shape much. This helps the chamber stay strong when it gets hot. Graphite spreads heat well and does not react with chemicals. It helps keep the heat even inside the vacuum.
Vacuum furnace chambers can be all-metal, all-graphite, or mixed. All-metal hot zones have thin metal shields with vacuum spaces. These shields reflect heat and stop it from escaping. Molybdenum shields are closest to the heat. Stainless steel gives extra support behind them. Some furnaces use tantalum or tungsten for even higher heat. The chamber material changes how well the furnace keeps heat, how hot it gets, and how long it lasts.
Note: Good chamber materials help the vacuum furnace keep a steady vacuum and give accurate heat treatment.
Heating Elements
Heating elements give the heat needed in vacuum furnaces. The type depends on how hot the furnace needs to get. Nickel-chromium and iron-chromium-aluminum alloys work for lower heat. These alloys are cheap and last a long time. For higher heat, furnaces use molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite. These can handle very high temperatures and stay strong.
| Heating Element Types | Temperature Range | Advantages / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium, Iron-Chromium-Aluminum | Up to 1000°C | Affordable, good for lower temperature vacuum furnaces |
| Molybdenum, Tungsten, Graphite | Above 1200°C | High melting points, stable at high temperatures |
| Graphite, Tantalum | Up to 2200°C | Excellent for very high-temperature vacuum furnace applications |
Graphite heating elements are now common in vacuum furnaces. They last a long time and do not break from quick heat changes. They work well in a vacuum. Molybdenum elements also work at high heat but need careful use. The right heating element helps the furnace heat up evenly and quickly.
Vacuum System
The vacuum system makes the low-pressure space inside the furnace. It uses different pumps to do this job. First, a roughing pump lowers the pressure. Then, a diffusion pump or another high-vacuum pump lowers it even more. Some furnaces can reach very low pressures for special jobs.
Workers check the vacuum with bake-out cycles and leak tests. A good furnace keeps leaks under 20 microns per hour. The best ones keep leaks under 5 microns per hour. Teams check seals, change pump oil, and watch the cooling water. These steps help the vacuum system work well. This lets the furnace give clean and repeatable results.
Tip: A strong vacuum system is important for good heat treatment. Checking and fixing it often keeps the furnace working well.
Temperature Control
Temperature control is very important in vacuum furnaces. Modern vacuum furnaces use computers to control the heat. These computers watch the temperature inside the chamber. They change the power to the heating elements when needed. Workers use thermocouples in different places to check the heat. This helps all parts get the same heating and cooling.
Good temperature control makes things safer and better. Oxygen probes check the air inside the furnace. This helps stop oxidation. Engineers use simulators to test heat treatment plans before real work. This lowers mistakes and helps make the process better. Vacuum and gas-pumped furnaces keep the air steady. This protects the material from getting dirty.
The table below shows important features for good temperature control in vacuum furnaces:
| Feature Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Multi-zone thermocouples help check temperature in many spots; heat stays within ±5°F |
| Advanced Control Systems | PLCs and SCADA give alerts, keep records, and save data |
| Atmosphere Control | Using vacuum or special gas stops oxidation and keeps materials safe |
| Temperature Uniformity | Insulation, sensors, and controlled air or gas flow keep heat even |
| Safety Systems | Over-temperature protection, inert gas, safety stops, and clean designs help keep things safe |
| Integrated Quenching | Fast cooling keeps alloys strong |
| Recipe Management | Special programs and batch records help track each part |
Vacuum furnaces can get as hot as 3,000°C. Their smart temperature systems keep the process steady and the same every time. These features make vacuum furnaces important for jobs like making airplane and electronic parts. Even small changes in heat can change how good the products are.
Note: Good temperature control in a vacuum furnace helps make better materials and keeps the furnace working longer.
Types of Vacuum Furnaces
Single-Chamber
A single-chamber vacuum furnace has one sealed area for all steps. Workers put parts inside, remove the air, heat, soak, cool, and take out the parts. Everything happens in this one chamber. This design is easy to use and many people know it. It works well for small or medium jobs and when you need to change things often.
But there are some problems with this type. The whole chamber must heat up and cool down every time. This means you have to wait between batches. It also uses more energy. Heating and cooling again and again can hurt the chamber. This can mean more repairs. These furnaces need strong pumps to get the right vacuum after each use.
Note: Single-chamber vacuum furnaces are simple and good for many jobs, but they might not be best for big or energy-saving factories.
Multi-Chamber
Multi-chamber vacuum furnaces have more than one chamber. Each chamber does a different job, like heating or cooling. This lets the hot zone stay at the same temperature. It saves energy and helps the parts last longer.
Multi-chamber furnaces can handle more work at once. Workers can move parts from one chamber to another. This makes the process faster and keeps the heat even. You can add more chambers if you need to make more parts. These furnaces often use computers to help control everything and keep records.
Here is a table that compares single-chamber and multi-chamber vacuum furnaces:
| Feature | Single-Chamber Vacuum Furnace | Multi-Chamber Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Cycle | The whole chamber does every step, so it takes longer. | Different chambers do different jobs, so it is faster. |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses more energy because it heats and cools the whole chamber. | Saves energy by keeping the hot zone warm. |
| Design Challenges | Must handle both heating and cooling in one place. | Each chamber can be built for its own job. |
| Thermal Cycling Effects | The chamber gets more stress and can wear out faster. | The hot zone stays steady, so parts last longer. |
| Throughput | Can only do a few loads at a time. | Can do more loads and keep the quality even. |
| Scalability | Need to buy another furnace to make more parts. | Just add more chambers to make more parts. |
| Vacuum Performance | Air gets in between batches, so it needs strong pumps. | The hot zone stays under vacuum, so it is easier to keep clean. |
| Overall Advantages | Simple and easy to use. | Saves energy, grows easily, and is good for making lots of parts. |
Multi-chamber vacuum furnaces are great for places that need to make lots of parts and want good control. They help save money on energy and make better products.
Continuous
Continuous vacuum furnaces move parts through different zones without stopping. They use belts or pushers to move parts from loading to heating and then to cooling. The vacuum stays steady the whole time. This keeps the temperature the same and treats every part evenly.
Continuous vacuum furnaces are good for making lots of parts fast. They are used in car, electronics, and green energy factories. Workers do not need to move each batch by hand. The machine does the work, which saves time and effort. This also means each part uses less energy.
Batch vacuum furnaces treat parts in groups. They are good for special jobs or when parts are different sizes. Continuous furnaces focus on speed and doing the same thing every time. They cost more at first and need more care, but they save energy and make more parts.
| Aspect | Batch Furnaces | Continuous Furnaces |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Treats parts in groups or batches | Parts move through the furnace without stopping |
| Material Handling | Uses baskets or racks for each batch | Uses belts or pushers, no baskets needed |
| Production Volume | Good for small or medium jobs | Best for making lots of parts all the time |
| Temperature Control | Can set the heat for each batch | Keeps the same heat for all parts |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses more energy for each part | Saves energy because it runs all the time |
| Maintenance | Needs less care and is easier to fix | Needs more care and is harder to fix |
| Applications | Good for special jobs or research | Good for big jobs with lots of the same parts |
Tip: Continuous vacuum furnaces help factories make lots of parts quickly and save energy at the same time.
Specialized Furnaces
Specialized vacuum furnaces do special jobs in factories. These furnaces can handle hard tasks that regular ones cannot. Engineers make them for certain jobs, like brazing, sintering, or chemical vapor deposition. They use smart controls and strong materials to meet tough rules.
Aluminum Brazing
Aluminum brazing furnaces are important for making heat exchangers and radiators. They also help make other aluminum parts. These furnaces create a vacuum so oxidation does not happen. This keeps aluminum clean and strong while brazing. The process joins aluminum pieces with a filler metal using high heat.
Some main features of aluminum brazing furnaces are:
- They can reach a high vacuum, from 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ Torr, for clean work.
- They keep the temperature even, often above 600°C, for good brazing.
- They have many heating zones for better heat control.
- They use special heating elements, like nickel-chromium or graphite.
- They have gas systems to add argon or nitrogen.
- They include safety systems, like locks and emergency stops.
These furnaces are used for many things:
- Making car radiators and condensers.
- Producing air conditioning parts.
- Making heat exchangers for electronics and new energy cars.
Note: Aluminum brazing in a vacuum furnace makes strong, leak-free joints and shiny, clean surfaces.
DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace
The DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace is a top choice for aluminum brazing. DAG made this furnace for making lots of parts with high quality. It uses a nickel-chromium heating system and a multi-layer 1Cr18Ni9Ti screen. This setup gives good and even heat.
Main features of the DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Three-stage: diffusion pump, Root pump, mechanical backing pump |
| Heating Elements | Nickel-chromium strips with reflective screen |
| Customization | External circulation air cooling, tailored chamber sizes |
| Temperature Range | Up to 800°C |
| Working Area | Models from 6100×1200×1200 mm to 9000×1550×1830 mm |
| Power Options | 750kW, 1000kW, 2000kW |
| Vacuum Level | Ultimate vacuum of 6.7×10⁻⁴ Pa |
| Cooling System | Negative pressure operation with gas cooling |
DAG’s furnace can make many aluminum parts:
- Air conditioners, oil coolers, and radiators.
- Evaporators and condensers.
- Radar antennas and waveguides.
- Plate-warped and tube-fin heat exchangers.
- Water-cooled plates and air-cooled boxes for electronics.
The furnace has advanced controls. Operators can set exact recipes for each batch. The system checks temperature, vacuum, and gas flow all the time. This helps get the same, high-quality results every time.
Tip: DAG’s custom options let companies pick the right furnace size and features for their needs.
Specialized vacuum furnaces like the DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace help factories make clean, strong, and reliable products. Their smart systems and flexible designs make them very useful for today’s factories.
Applications
Aerospace
The aerospace industry uses vacuum heat treatment furnaces for many jobs. These furnaces treat aluminum alloys in airplanes. The way the grains form in these alloys matters for how long planes last. Vacuum furnaces help control the grain shape.
- They keep out oxygen, so metals do not get dirty.
- Age hardening and artificial aging make alloys stronger at different heats.
- High vacuum brazing joins tricky parts with strong, clean seams.
- Normalizing makes the grain size better and lowers stress in metals.
- Tempering and hardening make steel parts tougher and stronger.
NASA uses vacuum heat treating to train and test workers. These steps help keep airplane parts safe and working well. The vacuum makes sure heating and cooling are even, which is very important.
Note: Vacuum heat treatment helps keep aircraft safe and high quality by stopping oxidation and dirt during work.
Automotive
Vacuum heat treatment furnaces are important for making car parts. They make metal surfaces better and stronger. The vacuum keeps parts clean and shiny. Even heating stops bending and helps parts last longer.
| Automotive Components | Purpose of Vacuum Heat Treatment |
|---|---|
| Gears | Make them stronger and last longer |
| Shafts | Help them stay strong and not wear out |
| Springs | Make them bend well and last longer |
| Bearings | Make them harder and stronger |
| Pistons | Make them harder and stop wearing out |
| Crankshafts | Help them stay tough and strong |
| Connecting rods | Make them strong and stop breaking |
| Axles | Help them stay strong and last longer |
| Chains | Make them strong and stop wearing out |
| Transmission parts | Help them work smoothly and not break |
Vacuum furnaces also help with carburizing and nitriding. These steps make parts stronger and harder to wear out. The clean space keeps out dirt, which is important for fast cars.
Electronics
Vacuum heat treatment furnaces help make electronic parts and devices. They give a clean place to make pure materials. This stops oxidation and dirt during sintering and brazing.
- These furnaces help semiconductors and power circuits work well.
- Vacuum sintering gives exact heat control and even heating.
- Special tools inside hold parts in place and press them right.
- Forced cooling systems control how fast parts cool, which helps joints.
Vacuum furnaces make electronic parts better and last longer. They let companies use clean, repeatable steps for making lots of parts. The controlled space helps meet tough rules for how things must work.
Medical Devices
Vacuum heat treatment furnaces are very important for making medical devices. Companies use these furnaces to make implants, dental parts, and tools for surgery. The vacuum takes away dirt and other things from the chamber. This is needed to keep the devices safe for the body and follow health rules.
Metals like stainless steel and titanium alloys often get vacuum heat treatment. The process takes out oxygen, so the metal does not rust when it gets hot. This makes the metal stronger and helps it last longer. Medical devices must be strong and safe inside people. Vacuum heat treatment helps make sure of this.
The furnace keeps the temperature just right for each device. Even heating and cooling stop problems from happening. This also makes the metal harder and tougher. Different devices, like hip implants or dental screws, may need special treatment steps. The vacuum furnace can be set up for each kind.
Note: Vacuum heat treatment helps make medical devices that are safe, strong, and high quality by keeping the chamber clean and controlled.
New Energy
The new energy industry uses vacuum heat treatment for battery and fuel cell parts. These parts must work well in many different situations. Vacuum furnaces help test how parts act under different pressures and temperatures.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Importance | Vacuum heat treatment lets workers control pressure and temperature for battery and fuel cell tests. |
| Safety | Vacuum generators are used instead of pumps to stop sparks during hydrogen fuel cell tests. |
| System Functions | The system controls pressure, simulates temperature, measures mass, and collects data for good results. |
| Reliability | Keeping pressure and temperature steady makes new energy parts safer and work better. |
Vacuum heat treatment lets engineers test batteries for safety and fuel cells for how well they work. The process uses special tools to control pressure and check the vacuum. These tools help keep the furnace just right inside. The system also collects information about temperature, pressure, and how much mass is lost. This helps make batteries safer and better.
Tip: Vacuum heat treatment helps make new energy products safer and more reliable by letting workers test and control them carefully.
Aluminum Heat Exchangers
Vacuum heat treatment furnaces are needed to make aluminum heat exchangers for fast trains and cars. The process uses vacuum brazing to join aluminum pieces with strong, clean connections.
- Workers clean the aluminum parts to get rid of oil and dirt.
- They put fins and seals made from special aluminum into the furnace.
- The furnace removes air to make a strong vacuum, about 6×10^-3 Pa.
- The furnace heats the parts to about 605°C and keeps the temperature steady.
- Magnesium blocks inside help stop the aluminum from rusting during brazing.
- After holding at the right heat, the furnace cools the parts with nitrogen gas.
- Inspectors look at the finished heat exchangers to check for clean surfaces, strong joins, and no leaks.
- The finished products can reach up to 95% of the needed heat exchange ability.
Vacuum heat treatment makes sure aluminum heat exchangers are high quality. These exchangers are used in fast trains, cars, and other tough places. The process gives strong, reliable, and long-lasting parts.
Process Steps
Loading
Workers get the parts ready for heat treatment. They look at each part to make sure it is clean and not broken. Then, they put the parts on trays or racks. They leave space between the parts so heat can reach everywhere. The worker checks the chamber for any old dirt or leftover pieces. They follow the rules for loading to stop mistakes.
Before closing the chamber, the team checks that all sensors and thermocouples are in the right spots. They make sure the loaded parts match the plan for the batch. This helps keep things the same and easy to track. Training helps workers load parts safely and lowers risks. The worker closes the chamber door and checks that the O-rings and gaskets are clean and not damaged.
Tip: Loading parts the right way helps heat move evenly and stops problems.
Evacuation
After loading, the worker starts to remove air from the chamber. The vacuum system pulls out air and gases. This makes the low-pressure space needed for heat treatment. The worker watches the pressure gauges and controls. They look for leaks or strange numbers.
A three-stage vacuum system uses a mechanical pump, a Root pump, and a diffusion pump. Each pump makes the pressure lower than before. The worker checks for leaks with helium leak detectors or electronic tools. They look at seals and gaskets to keep the chamber clean. Keeping the vacuum system in good shape helps it work well.
Workers follow the rules for this step. They write down the vacuum levels and how the system is working. This helps fix problems and check quality later. Getting a good vacuum stops oxidation and helps make better parts.
Heating
When the chamber has the right vacuum, the worker starts heating. The furnace uses heating elements like nickel-chromium strips or graphite rods to get hot. Automatic controls set how fast and how much the furnace heats up. Workers watch the temperature sensors and change settings if needed.
The heat treatment needs the right temperature at all times. Multi-zone thermocouples check heat in different places inside the chamber. The worker follows the heating plan for the type of part and material. Tools that check the heaters help find problems early.
Even heating makes sure every part gets the same treatment. The worker looks for alarms or anything strange during heating. They write down the temperature for each batch. This helps keep track and make the process better.
Note: Getting the heat just right is very important for strong and good parts.
Cooling
Cooling is an important part of vacuum heat treatment. After heating, the furnace must cool the parts slowly and safely. The system uses gas or outside air to take away heat. Operators pick the best cooling way for each metal and product.
The furnace often uses gases like nitrogen or argon. These gases go into the chamber and pull heat from the parts. The cooling system can change how much gas moves and how strong it is. This helps control how quickly the parts get cooler. Some furnaces use fans to move the gas faster.
Even heating and cooling stop cracks and bending. The system keeps the temperature change the same for all parts. This helps every part stay strong and keep its shape. The operator checks sensors and controls to make sure cooling goes as planned.
Tip: Cooling the right way keeps the metal good and stops problems.
Unloading
When the parts are cool enough, the operator opens the chamber. The team checks the pressure and temperature before taking out the parts. Workers wear gloves and safety gear to stay safe. They lift out trays or racks carefully so nothing breaks.
Operators put the cooled parts on clean tables or trays. They look at the parts to see if anything is bent or broken. The team writes down the batch number and other details to keep track. Good unloading keeps the parts clean and ready for the next step.
- Check the chamber before opening it
- Wear safety gear when touching hot parts
- Put parts on clean trays or tables
- Write down batch details to keep records
Quality Control
Quality control makes sure every part is good enough. Inspectors look for cracks, stains, or other problems. They use tools like calipers, hardness testers, and microscopes. The team checks if the parts match what is needed for each product.
A table helps keep track of quality checks:
| Checkpoint | Tool Used | Pass/Fail Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Surface finish | Visual/Microscope | No cracks or stains |
| Hardness | Hardness tester | Within set range |
| Dimensions | Caliper | Matches blueprint |
The operator looks at the data and signs off on the batch. If a part does not pass, the team puts it aside for more checks. Good quality control keeps customers happy and stops waste.
Note: Careful checking here helps make sure every product works well.
Considerations for Vacuum Furnaces
Material Compatibility
Material compatibility is very important when picking vacuum furnaces. Different metals, like steel, aluminum, and titanium, act differently with heat. Each metal has its own melting point and expands at a different rate. A furnace that works for steel might not work for aluminum. Every material needs its own heat and how the heat spreads.
Not all materials change the same way when heated or cooled. Knowing how each one acts helps engineers stop problems and make better products. Some alloys can bend or crack if the furnace does not fit their needs. The shape of the part, how it is put in, and how long it should last also matter.
When picking materials for vacuum heat treatment, think about these things:
- The right temperature range for the material.
- If the material stays stable after many heat cycles.
- How much the material grows or shrinks with heat.
- How making the part changes its chemical makeup.
- Design details, like how it is held or loaded.
- How long the part needs to last.
- What the material will face inside the vacuum.
- If the material is easy to get and how much it costs.
Choosing an alloy often depends on how strong it is at high heat and if it can handle chemicals in a vacuum. Engineers look at how well the material holds up under stress and heat. Picking the right process for the material helps make strong and safe parts.
Tip: Always use the right furnace and process for the material to get the best results.
Temperature Range
The temperature range tells what jobs a vacuum furnace can do. Each material needs a certain heat to work best. For example, aluminum needs less heat than steel. If the furnace cannot get hot enough or stay at the right heat, the job might not work.
Vacuum furnaces have systems to keep the heat steady and even. This stops the parts from getting too hot or too cold. Engineers must check the highest and lowest heat the furnace can reach before starting.
Here is a table that shows some materials and their heat ranges:
| Material | Typical Heat Treatment Range (°C) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 350 – 600 |
| Steel | 800 – 1300 |
| Titanium | 600 – 1000 |
Picking a furnace with the right heat range keeps the process safe and works well.
Vacuum Level
Vacuum level means how much air and gas is taken out of the furnace. A high vacuum means almost no air is left inside. This is important because air and gases can make the metal dirty or cause rust during heating.
Vacuum furnaces use special pumps to get the right vacuum. The best vacuum depends on the job and the material. Some parts, like shiny alloys, need a higher vacuum. Jobs that are not as hard may use a lower vacuum.
Workers watch the vacuum level during the whole process. They look for leaks and make sure the vacuum stays steady. Keeping a good vacuum helps the metal stay clean and gives the same results every time.
Note: Picking the right vacuum level keeps materials safe and makes better products.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is very important when picking a vacuum heat treatment furnace in 2025. Companies want to use less energy to save money and follow new rules. New vacuum furnaces are built to waste less energy. They have better insulation, smart controls, and strong heating parts that use less power.
Many factories use computers and digital tools to watch how much energy they use. These tools help workers change heating and cooling times. They also find problems early, so the furnace keeps working well. IoT lets teams watch energy use live and make fast changes to save power.
The table below shows how energy efficiency helps vacuum furnace work:
| Factor | Impact on Operations |
|---|---|
| Improved Insulation | Keeps heat in and lowers energy bills |
| Smart Controls | Makes heating and cooling work better |
| Efficient Heating | Needs less power for the same job |
| IoT Monitoring | Watches energy use and finds waste |
| Automation | Lowers mistakes and saves more energy |
Energy-efficient furnaces help companies follow green rules. Using less energy means less pollution and helps the earth. Many people now want furnaces with green features. These can be emission control systems or ways to use clean energy.
Tip: Picking an energy-efficient vacuum furnace can save money over time and help companies reach green goals.
Energy costs are a big part of running a vacuum furnace. Companies that buy efficient furnaces save money in the long run. They also find it easier to follow new energy and pollution rules. As more people buy furnaces, energy efficiency will stay important for all companies.
Vacuum heat treatment helps companies make metal parts better. The furnace keeps metal surfaces clean and strong each time. When people know how the furnace works, they can pick the best way to treat metal. Many businesses now want new machines like the DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace. Companies that buy new vacuum heat treatment technology will be ahead as the industry gets bigger.
FAQ
What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace used for?
A vacuum heat treatment furnace changes metals and alloys. It makes them stronger and harder. It also helps the surface look better. Many companies use these furnaces to make parts with clean and strong surfaces.
How does a vacuum prevent oxidation during heat treatment?
The vacuum takes out air and gases from the chamber. Without oxygen, metals do not get rusty or form scale. This keeps the metal surface shiny and clean.
Which industries use vacuum heat treatment furnaces most?
Aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical, and new energy companies use these furnaces. They need metal parts that are strong and work well.
What materials can be processed in a vacuum furnace?
Steel, aluminum, titanium, and some ceramics can go in a vacuum furnace. Each one needs its own heat and vacuum level to work best.
How does the DAG Giant Vacuum Aluminum Brazing Furnace stand out?
DAG’s furnace has special heating and a three-stage vacuum system. It comes in different sizes and has strong controls. Many companies use it for making aluminum heat exchangers and electronic parts.
What safety features do modern vacuum furnaces include?
Modern furnaces have automatic controls, emergency stops, and sealed chambers. These things help keep workers safe and protect the process.
How does automation help in vacuum heat treatment?
Automation controls the heat, vacuum, and timing. It helps stop mistakes and keeps every batch the same. Workers can watch the process as it happens.
Why is energy efficiency important in vacuum furnaces?
Energy-efficient furnaces use less power and make less pollution. Companies save money and follow green rules by using less energy.