Air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condenser machine types help factories work better today. Picking the right condenser machine affects how well things run, how often they break, and how much they cost. Lately, more people choose air-cooled models because water is hard to find and they are easier to take care of. But water-cooled and evaporative types are still needed for big jobs with lots of heat. Companies now use advanced radiator making machine solutions like the Radiator Fin Forming Machine to make sure their work is exact and can change for tough jobs.
Key Takeaways
- Air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condenser machines all have special strengths. Each type works best for different jobs in factories. Air-cooled condensers do not use much water and are simple to set up. They work well in dry places and for easy projects. Water-cooled condensers use less energy and make less noise. They are best for big factories that have lots of water. Evaporative condensers use both air and water to cool things down. They save energy and are good for hot places with little space. You need to clean coils and check parts often to keep condenser machines working well and lasting long. The DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine helps make radiators faster and more accurately. It can shape fins for many kinds of materials. Picking the right condenser machine depends on how much cooling you need, how much space you have, if you have water, how much energy you want to use, and how much maintenance you can do. DAG gives strong help, custom options, and safety features. This helps factories make more products and keeps workers safe.
Industrial Condenser Machine Overview
Types of Industrial Condenser Machines
Factories use three main condenser machine types. These are air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative. Each type removes heat from refrigerant vapor in its own way. This is important for hvac and air conditioning systems. The way these machines are built and work is different. This makes each one better for certain places and jobs.
| Aspect | Air-Cooled Condenser | Water-Cooled Condenser |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Uses outside air to get rid of heat | Uses water that moves around refrigerant coils |
| Cooling Method | Air blows over the condenser coils | Water takes in heat, then cools down somewhere else |
| Condensing Temperature | Depends on dry air temperature; higher when hot | Depends on wet air temperature; usually lower |
| Efficiency | Not as efficient, changes with air temperature | More efficient because water moves heat better |
| Water Usage | Does not need water | Needs a lot of water and a cooling system |
| Installation & Use | Easier to set up, but needs good air | Harder to set up, needs pumps and cooling towers |
| Applicable Environment | Good where water is hard to get | Good where water is easy to get and quiet is needed |
Evaporative condenser machines use both air and water to cool. This makes them cool refrigerant better than air-cooled machines, especially when it is hot. There are two main ways they work. In combined flow, air and water move together over the coil. In counterflow, air goes up and water sprays down. These machines use axial or centrifugal fans. Induced draft fans pull air from the top. Forced draft fans push air from the bottom.
Key Features and Applications
Industrial condenser machines are important for hvac and air conditioning. They cool refrigerant vapor and turn it back into liquid. The kind of condenser machine you pick changes how well it works, how often it breaks, and how much it costs.
Tip: Clean the coils and check for clogs often. This helps save energy and makes the machine last longer.
Some important things to think about are:
- How much cooling it can do and how much power it needs
- What refrigerant it uses and if it works with your hvac system
- How strong it is and what it is made of
- How much energy it saves, like EER, COP, and IPLV
- If it has smart controls, like variable speed drives
- How easy it is to fix and keep clean
- If it is safe and follows the rules
Different industries use different condenser machines for their needs. Air-cooled condensers are good for geothermal power plants and small chiller plants. They are best where water is not easy to find. Water-cooled condensers are used for big heat pumps and factories with cooling towers. Evaporative condensers are used in process industries and big heat pumps that need to get rid of a lot of heat. Hvac makers choose the right machine based on the job, place, and what they want to achieve.
Comparison Table: Top 3 Industrial Condenser Machines
Specifications
Industrial condenser machines come in many sizes. They can handle many jobs in hvac. The table below lists the main details for top air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condenser machines.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Capacity Range | 50 to 3,714 nominal tons |
| Size Options | 7-foot wide single and multi-cell box sizes, easy for containerized export shipments |
| Coil Technology | Thermal-Pak II® Coil with CrossCool™ Internal Tube Enhancement for better heat transfer |
| Construction Materials | Stainless steel options for coils, basin, casing, and fan section |
| Additional Features | Drift eliminators, air inlet louvers, pressurized water distribution, sound attenuation |
| Power Consumption | Varies by model and application |
Note: These details help hvac makers pick the right condenser machine for each factory.
Performance Metrics
Performance is very important in hvac. Factories want machines that cool well and save energy. The table below compares the main performance numbers for air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative systems.
| Metric | Air-Cooled System | Water-Cooled System | Evaporative System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Energy Efficiency | 1.13 – 1.25 kW/ton | 0.58 – 0.79 kW/ton | Improves COP by 6%–91%* |
| Compressor Pressure Differential | ~98 PSI | ~53 PSI | Lower than air-cooled |
| Energy Consumption | About twice water-cooled | Baseline | Up to 8.2% less than air-cooled |
*Evaporative cooling can make COP up to 91% better than air-cooled chillers. Water mist systems can lower chiller power use by 8.2% and raise COP by 30%. This works best in dry places. These results depend on temperature, humidity, air speed, water spray, and refrigerant type.
- Air-cooled systems are best where water is hard to get.
- Water-cooled systems save energy and work for big hvac plants.
- Evaporative systems are a strong choice for saving energy.
Feature Highlights
Each condenser machine type has special features. The table below shows what makes top models stand out in the hvac world.
| Company/Brand | Unique Features and Innovations |
|---|---|
| Johnson Controls | Wide product range, YORK YLAA Air-Cooled Scroll Chillers, strong R&D, global reach |
| Emerson Electric Co. | Vilter and Copeland compressors, 21 innovation centers, Box Load Calculator, high-performance lubricants |
| GEA Group | Focus on advanced engineering, supports many hvac manufacturers, strong in process industries |
- Johnson Controls has many products and new air-cooled chiller models.
- Emerson Electric Co. helps hvac makers with innovation centers and compressor technology.
- GEA Group works with hvac makers in process industries and gives engineering help.
Tip: Hvac makers should match machine features to their plant’s needs for the best results.
Air-Cooled Condenser Machines

Overview
Air-cooled condenser machines are important in hvac and air conditioning. They use outside air to cool refrigerant. Many factories and big buildings pick them. These machines do not need water. This makes them good for dry places. Fans blow air over finned coils to take away heat. This helps the refrigerant cool down. This way saves energy and stops scaling or rust. Companies like these machines because they are easy to set up. They do not need much care. They also do not have water problems.
Note: Air-cooled condenser machines save water and help the environment.
Leading Model: Daikin Air-Cooled Condensing Unit
Performance
The Daikin DRC0603D000001S is a top hvac machine. It cools about 60,000 BTUs each hour. This is good for big stores and factories. It keeps cooling even when it is hot outside. Many people say it works well in factories. It keeps rooms cool and safe. The unit uses R-32 refrigerant. This helps it work well and follow green rules.
Efficiency
Daikin’s air-cooled unit has a 16.2 SEER2 rating. This means it uses less power to cool big spaces. Many people see lower bills after using this unit. Its design fits well in energy-saving hvac systems. It is a smart pick for companies that want to save money and help the planet.
Durability
This model meets ASHRAE and EPA rules. It is made from strong parts that do not rust. The fans and coils last a long time if you take care of them. Cleaning filters and checking the unit helps it work for years. It is also quiet, so it does not make much noise at work.
Pros and Cons
| Advantage/Disadvantage | Description | Industrial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Water-saving | Does not use water, so it helps the planet | Works well in dry places and saves water money |
| Easy Installation | Simple build and needs little care | No hard pipes or water cleaning needed |
| Scaling Resistance | No water means no scaling | Less time stopped and fewer fixes |
| Operational Independence | Can work in far or special places | Good for places that are hard to reach |
| Large Footprint | Needs more space to get rid of heat | May not fit in small factories |
| Cooling Efficiency | Not as strong as water-cooled, especially when it is hot | May not cool fast enough in very hot times |
| Noise | Big fans can be loud | May need noise fixes in quiet places |
| High Initial Cost | Costs more at first than water-cooled units | Big units cost more at the start |
Best Industrial Applications
Factories use air-cooled condenser machines in many ways. They are used in commercial fridges to keep food safe. These machines also help cool process fluids and lube oil. They work in closed loop cooling too. Chemical and oil plants use them to avoid water costs and leaks. Air-cooled condensers are good where water is rare or costly. Their design fits big cooling and air systems. This makes them a top pick for factory cooling.
Water-Cooled Condenser Machines
Overview
Water-cooled condenser machines are important in hvac for big buildings and factories. These machines use water to take heat from refrigerant vapor. The heat then moves away through cooling towers or heat exchangers. Water-cooled condensers are usually inside, so weather and dirt do not hurt them. This helps them last longer and stay quiet. Many engineers pick water-cooled systems because they work well and save energy. They are good for places with little space or where it must be quiet.
Water-cooled condensers keep cooling well, even if the weather changes.
Leading Model: Sterling TT Water-Cooled Condenser
Performance
The Sterling TT water-cooled condenser is a top hvac machine. It gives steady cooling for big jobs. This model uses special heat exchanger technology to keep pressure low. Lower pressure means it works better and uses less energy. Power plants and factories trust this model to keep things running, even when busy.
Efficiency
Water-cooled condensers like the Sterling TT save energy because water cools better than air. This model uses water’s strong heat power to keep things cool. This helps factories and power plants spend less on energy. Studies show water-cooled systems can use half the energy of air-cooled ones. That is why they are a smart pick for big hvac jobs.
Durability
Sterling TT makes its water-cooled condensers with strong, rust-proof parts. These machines do not get hurt by weather or outside damage. They are made to go inside, so they last longer. Many people say these machines work well for years if you take care of them.
Pros and Cons
- Advantages:
- Lasts a long time because it is inside and made strong
- Runs quietly without big fans or vents
- Saves energy and cools well
- Can fit in small or tight rooms
- Uses water, which is safe for cooling
- Disadvantages:
- Costs more to buy and set up
- Needs more care, like cleaning and water treatment
- Harder to set up and needs skilled workers
- Not good for places with little water
- Does not work as well in wet, humid places
Best Industrial Applications
Water-cooled condenser machines help many kinds of factories. Steam power plants, even nuclear ones, use them to lower pressure and work better. Big hvac and fridge systems in factories need water-cooled condensers for steady cooling. Research shows these machines help move heat and water better in process jobs. They are quiet and small, so they are good for hospitals, data centers, and other quiet places. Water-cooled condensers are still a top choice for cooling in places with enough water and where good performance matters.
Evaporative Condenser Machines
Overview
Evaporative condenser machines are important in many hvac systems. They use air and water together to cool refrigerant vapor. This helps remove heat well, even when it is hot outside. Factories and big buildings pick evaporative condensers because they do not need much space. The design saves energy and keeps noise low. These machines are flexible and do not need lots of fresh air to work.
Operators should test water and clean the system often. This keeps the machine working well.
Leading Model: Goodway Technologies Evaporative Condenser
Performance
The Goodway Technologies evaporative condenser is a top hvac machine. It cools refrigerant gas fast and keeps the temperature steady. Its small size fits in tight spaces at busy factories. The machine works well in hot places and cools large loads easily.
Efficiency
This model is very efficient, especially in dry places. It uses less energy than many air-cooled machines. Operators pay less for power and get better cooling. The design has fewer open parts, so it lasts longer and runs quietly. Many hvac workers like this model for its good performance and energy savings.
Durability
Goodway Technologies makes its evaporative condensers with strong materials. The closed design keeps important parts safe from harm. The machine does not rust and can handle heavy use in factories. Cleaning and treating the water stops scale and algae, so the system stays in good shape for years.
Pros and Cons
- Strengths:
- Cools refrigerant gas well
- Small size saves space
- Very efficient in hot, dry places
- Fewer open parts for longer life and quiet use
- Works well in high heat
- Can be placed in many spots
- Weaknesses:
- Needs regular cleaning and water care
- Uses a lot of water, which is hard in dry areas
- Does not work as well in humid weather
- Costs more to set up because of extra pumps and towers
- Needs steady water and good water quality
- Can get scale, algae, leaks, or freeze in cold weather
Best Industrial Applications
Evaporative condenser machines help many types of businesses. They keep food cold in storage buildings and help power plants stay cool. Chemical plants use them for exact cooling. Data centers use these machines to stop servers from getting too hot. Stores, hotels, and offices use them for hvac and refrigeration.
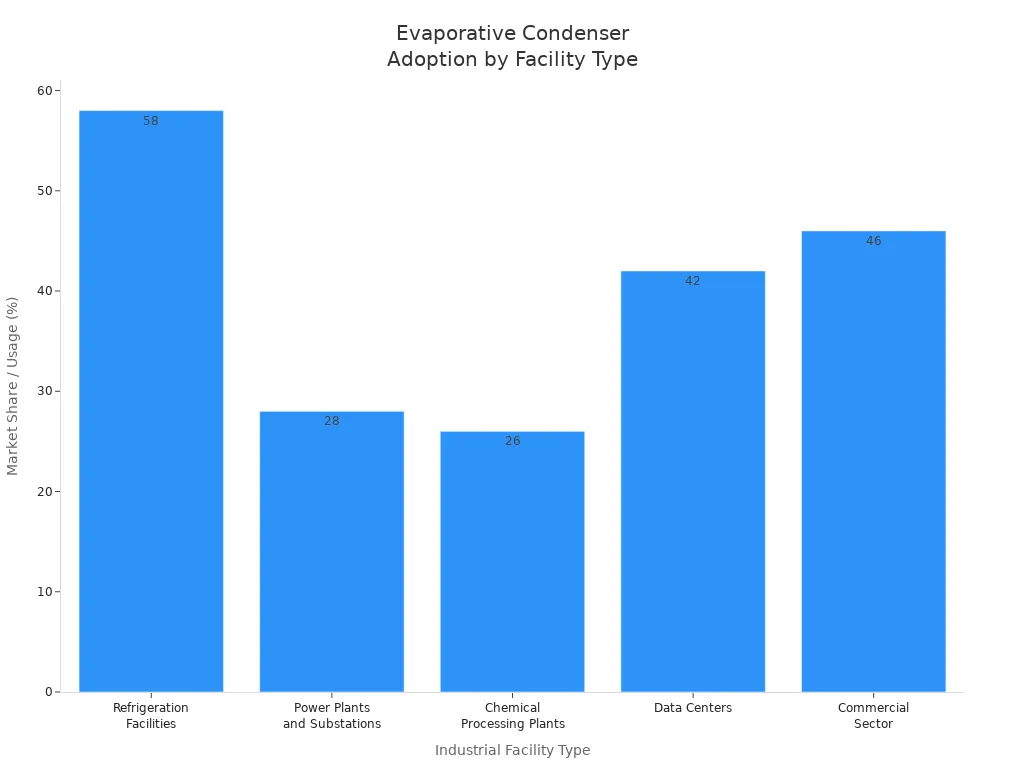
| Industrial Facility Type | Market Share / Usage % | Key Benefits and Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigeration Facilities | 58% of market | Used in food storage, cold chain logistics, meat processing; 49% of cold storage facilities use these units; up to 28% energy savings vs air-cooled systems. |
| Power Plants and Substations | 28% of market | Thermal plants and renewable energy facilities use evaporative condensers for heat dissipation; 32% of thermal plants in NA and Europe integrated these units; improve energy transfer efficiency and reduce water usage. |
| Chemical Processing Plants | 26% of market | Used in cooling towers, process heat rejection, chemical storage; 37% of large chemical plants report improved thermal regulation; corrosion-resistant and ammonia compatible. |
| Data Centers | Part of air conditioning segment (42%) | Provide 31% more efficient thermal management; help maintain server performance and reduce cooling costs. |
| Commercial Sector (Supermarkets, Restaurants, Hotels, Malls, Offices) | 46% of global usage | Adopted for HVAC and refrigeration; 44% of food retail chains replaced air-cooled systems; 33% of urban commercial projects use evaporative systems. |
Evaporative condenser machines help many industries meet their cooling needs. Their strong performance and flexible design make them a top pick for modern hvac systems.
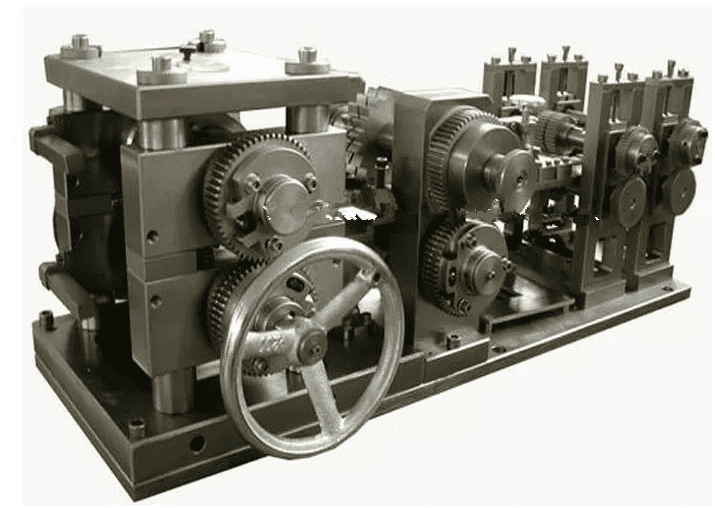
DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine for Industrial Use

Product Overview
The DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine is a very accurate tool for making radiators. It can make many types and sizes of radiator fins. This makes it a good choice for different factories. DAG made this machine for modern factories that need fast and exact work. You can use it with both aluminum and copper. This helps companies keep up with what customers want. The machine is built strong, so it lasts a long time, even in tough places. DAG also gives expert help and helps set up the machine at your factory. This lets companies start using it quickly and easily.
Key Features
The DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine has many smart features that help make work faster and better:
- It can run very fast, up to 100 meters each minute.
- It can cut up to 60 times every minute for quick work.
- You can change the plate length for different radiator shapes.
- It works with aluminum foil (3003-H16) and copper (H62).
- You can swap rollers to make straight, wavy, or other fin shapes.
- It can make fins from 0.07 to 0.08 mm thick and 8 to 200 mm wide.
- It uses a smart PLC system and servo motors for exact moves.
- Air and electric parts keep flat tubes safe while making fins.
- The controls are easy to use and simple to understand.
- It does not need much fixing and has good safety parts.
- You can connect it with other machines for smooth work.
Tip: You can change the rollers fast, so it is easy to make new fin types without waiting a long time.
Performance and Efficiency
DAG’s machine works well in big factories. The smart PLC system and servo motors help it move just right. This means fewer mistakes and good fins every time. It can make a lot of fins quickly, so factories can make more products. You can use it for radiator cores from 150 mm to 800 mm. This lets you make many different radiator designs. The machine is fully automatic, so workers do not have to do much by hand. This helps stop mistakes and keeps the work going for a long time. The strong build, made with laser cutting and CNC bending, makes it last and stay exact. Many people say the machine is easy to use and works well. DAG also helps if you have problems after you buy it. Because it is fast, exact, and works with many materials, this machine is a great tool for any factory that makes radiators.
Customization and Versatility
DAG made the Radiator Fin Forming Machine to fit many factory jobs. The machine lets workers pick from lots of settings. They can use different rollers and change how the machine works. This helps them make fins for special cooling jobs. Many customers want fins in special sizes and shapes. The machine can make straight, wavy, louvered, serrated, or perforated fins. This means factories can make things for cars, HVAC, and data centers.
- Workers can use both aluminum and copper.
- The machine changes fast for new fin types.
- Smart controls like PLC and touch screens help workers.
- Automation lets the machine handle new jobs easily.
DAG’s machine uses new tech like IoT and AI. These tools help workers watch how the machine runs and make quick changes. The machine can work fast, up to 600 mm each minute. This helps factories fill big orders. All these choices help make special cooling systems, like for liquid cooling or data racks.
Factories can meet special customer needs and save energy because the machine is flexible.
Safety and Maintenance
DAG makes safety and easy care very important. The Radiator Fin Forming Machine has shields to keep workers safe. The design helps stop accidents and keeps people safe at work. Safety sensors and stop buttons give extra help.
It is easy and quick to take care of the machine. The parts are strong and last a long time. Workers can get to important spots for cleaning or checks. The PLC system watches the machine and tells workers if it needs care. This means less time stopped and more time working.
- Shields cover moving parts to keep workers safe.
- Sensors find problems early.
- It is easy to reach places that need care.
- The design means fewer repairs are needed.
Checking and cleaning the machine often helps it work well and last longer.
Integration with Industrial Production Lines
DAG built the Radiator Fin Forming Machine to work well with other machines. It uses PLC controls, servo motors, and air systems to work right. Factories can link this machine to other machines for full automation.
- The design lets workers change products fast.
- Programmable controls help make many things.
- Automation with AI and IoT checks quality as it works.
DAG gives OEM and ODM help so factories can use the machine with their own lines. Linking machines brings many good things:
- Faster work and better use of time
- Better and more even products
- Less need for workers and safer jobs
- Quick changes for new jobs
When machines work together, factories can make things faster, safer, and better. This helps companies keep up in a busy market.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Condenser Machine
Assessing Industrial Requirements
Picking the best condenser machine starts with knowing what your project needs. Engineers check many things before they choose. The table below shows the main things to think about:
| Criterion | Explanation |
|---|---|
| First cost | Money needed at the start for design, equipment, and setup |
| Suitability | If the machine fits the job and building |
| Constructability | How easy it is to buy, set up, and plan |
| Operations and Maintenance Ease | How simple it is to fix and change parts |
| Total cost of ownership | All costs over time, like fixing and energy |
| Manufacturer reputation | If the maker is trusted and has a good record |
| Impact on building design | Space needed and how it works with other systems |
| Noise criteria | If it meets noise rules, especially in quiet places |
| Lifespan | How long it will last and when to replace |
| Energy benefits | How well it saves energy and follows energy rules |
| Scalability and modularity | If it can grow or change for new needs |
| Redundancy and failure risk | If it has backups and how often it might stop |
| Environmental health attributes | If it uses safe materials and refrigerants |
| Safety | How it keeps workers and property safe |
Tip: Engineers should talk about these things with everyone on the project. This helps make sure the machine is right for all needs.
Comparing Machine Types
Each condenser machine type has its own good points. Air-cooled machines are good where there is not much water and setup must be easy. Water-cooled machines save more energy and are quieter. They are good for big buildings or places that need less noise. Evaporative condensers use both air and water. They cool well in hot places and fit in small spaces.
- Air-cooled: Easy to set up, no water needed, takes up more space.
- Water-cooled: Saves energy, quiet, needs water and water care.
- Evaporative: Small, saves energy, needs water care often.
Engineers look at these types and match them to the place, what is there, and what the project wants. They also think about how each type works with other machines and if it can be made bigger later.
Matching Features to Applications
Picking the right features for the job helps the machine work best. For example, a data center may need a quiet machine with backup parts. A food plant may need parts that do not rust and are easy to clean. Engineers look at these things:
- How much cooling it can do and how much energy it uses
- If the materials work well with the job
- Control systems for easy use and checking
- Safety parts to keep workers safe
- How easy it is to fix and change parts
Choosing the right features helps the machine do its job well. Engineers also think about the place, like if it is very hot or has chemicals, to pick a machine that lasts and stays safe.
Note: Picking features that fit the job helps the machine work longer and saves money.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Factories need to plan for both cost and care when using condenser machines. Companies should think about all the money they will spend, not just the price to buy the machine. This means looking at setup, energy use, water, and how much work it takes to keep the machine running.
Comparing Cost Factors
| Aspect | Air-Cooled Condenser | Water-Cooled Condenser |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Air | Water |
| Cooling Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Water Usage | None | Continuous supply needed |
| Maintenance | Less frequent, easier access | Regular, prevents scale and algae |
| Space Requirement | Smaller footprint | Larger, needs cooling tower and piping |
| Noise | Quieter operation | Noisier due to pumps and fans |
Air-cooled condensers are cheaper to set up. They do not need water pipes or cooling towers. This saves space and money. These machines use no water, so bills are lower. It is easy to take care of them. Workers can get to parts and clean them fast. Many companies pick air-cooled units if water is expensive or space is tight.
Water-cooled condensers cost more to buy and install. They need pumps, pipes, and cooling towers. These machines use a lot of water, so bills go up. They take more time to care for. Workers must look for scale, algae, and rust. If they skip these jobs, the machine may break or not work well. Water-cooled systems are best for big factories that need strong cooling.
Key Maintenance Steps
Doing regular care keeps condenser machines safe and working well. Companies should use a checklist to stop problems before they start:
- Look at supports and anchors to make sure they are tight.
- Check for rust on covers, tubes, and supports.
- Clean off scale from tube bundles to keep cooling strong.
- Look at fan parts for cracks, shaking, or loud sounds.
- Check shafts, bearings, mounts, belts, and bolts for damage.
- Clean drift eliminators and water sumps to stop clogs.
- Test safety switches for vibration.
- Check wires for loose ends or hot spots.
- Make sure spray nozzles are not blocked and spray right.
- Check valves for rust and to see if they work.
Companies should do these checks at least once a year. In tough places or with lots of use, checking more often helps stop breakdowns.
Planning for Long-Term Value
Smart companies think about more than just the first price. They plan for energy, water, and fixing costs. Air-cooled condensers need less care and have no water bills. Water-cooled systems cool better but need more work and water. Picking the right machine saves money and stops work from being delayed. Doing regular care helps the machine last longer and keeps things running well.
Why Choose DAG for Industrial Condenser Machine Accessories
Manufacturing Excellence
DAG is a top company for condenser machine accessories. They use new technology and check quality at every step. All machine parts must meet high standards. DAG makes machines with strong materials. This helps them last longer in hard factory jobs. They use laser cutting and CNC bending for exact parts. Skilled workers check each step in making the machines. DAG’s machines can work for many hours without stopping. Many hvac makers trust DAG because their machines keep running in busy places. The company tests every machine before sending it out. This makes sure customers get equipment they can trust.
DAG cares about quality, so factories do not lose time or money.
Customization Capabilities
DAG lets customers change many things on their machines. You can pick fin widths from 8 to 200mm. The machines work with many core sizes and both aluminum and copper. Smart PLC systems help users change settings fast. This means factories can switch jobs quickly.
- DAG gives OEM and ODM services for special brands or labels.
- Customers can pick different fin shapes and sizes.
- The machines work with both aluminum and copper cores.
- Automation makes it easy to add to factory lines.
- The smart PLC system lets you change settings fast.
- DAG’s machines run fast and can work for a long time.
- 24/7 tech support helps fix problems quickly.
DAG is different from IEA, LLC and SORADIATOR GROUP because they focus on automation and easy changes. This gives hvac makers more ways to use the machines. Many customers like how fast the machines work and the good help after buying. DAG’s choices help hvac makers do special jobs for their projects.
Support and Training
DAG gives great help and training to all customers. They help set up machines and give guides for new users. Skilled workers answer questions and fix problems fast. DAG teaches people how to use and care for the machines. This helps workers learn quickly and not make mistakes. The company also has online help and tips for fixing problems. Customers can get help any time, day or night. This good service helps factories keep working. Many hvac makers pick DAG because they know help is always there.
Good help and training let factories use their machines better.
Air-cooled condenser machines are popular because they use less energy. They also do not need much fixing, so they are good for most factories. Water-cooled units work best for big places like data centers. These units cool better and save more energy. Evaporative types are good for small spaces and cool things well.
- Condensing units help keep the right temperature in food, medicine, and HVAC jobs.
- Air-cooled models use less water and help save money.
DAG’s Radiator Fin Forming Machine lets factories make strong condenser parts. Picking the right machine features for each job gives the best results.
FAQ
What is the main difference between air-cooled and water-cooled condenser machines?
Air-cooled condenser machines use air to cool down heat. Water-cooled condenser machines use water to do this job. Air-cooled units are good for dry places. Water-cooled units work better in big factories and save more energy.
How often should factories maintain condenser machines?
Factories should check and clean condenser machines once a year or more. If the machines are used a lot or in tough places, they need more care. This helps stop problems and keeps the machines working well.
Can the DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine handle both aluminum and copper materials?
Yes. The DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine works with both aluminum and copper. This lets factories make many types of radiator fins. It helps meet different needs for each job.
Why do some industries prefer evaporative condenser machines?
Evaporative condenser machines save energy and fit in small spaces. They work well in hot and dry weather. Many companies pick them because they cool things fast and use less power.
What safety features does the DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine include?
The machine has shields to protect workers. It also has safety sensors and stop buttons. These parts help keep people safe at work.
How does automation improve radiator fin production?
Automation makes work faster and more exact. Machines like DAG’s model help stop mistakes and let workers change fin types quickly. This means more fins and better quality.
What factors affect the lifespan of a condenser machine?
How long a condenser machine lasts depends on care, how it is used, and what it is made from. Good care and fixing problems fast help machines last longer.
Can factories customize the DAG Radiator Fin Forming Machine for special projects?
Yes. Factories can change the fin width, height, and shape. DAG lets workers set the machine for special jobs and different products.