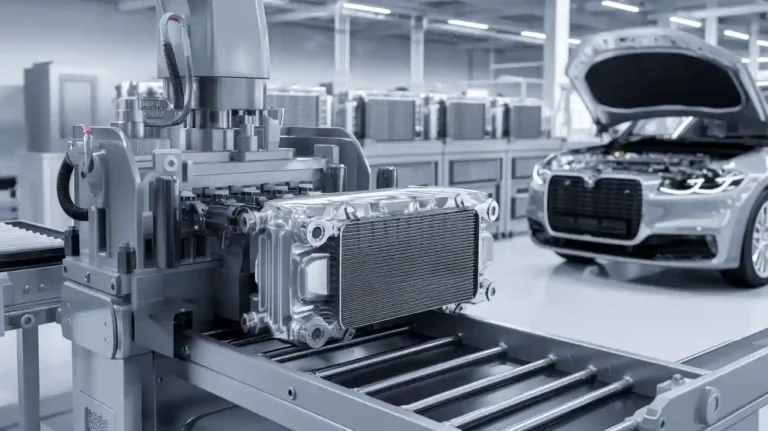
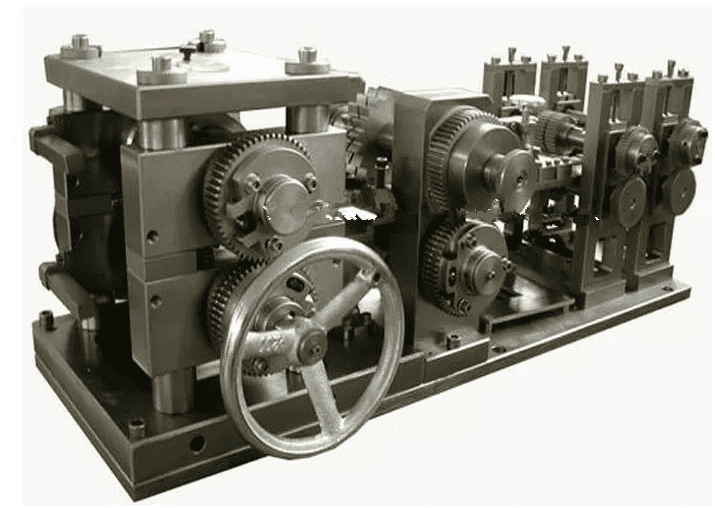
Radiator making machines are important for keeping car engines cool. These machines help make strong radiators that last a long time. New machine designs have changed how factories build radiators. Modern machines use advanced brazing, like vacuum brazing. This makes joints stronger and stops rust. Factories now use flat tubes with micro-channel and louvered fins. These parts help move heat better. Some machines, like the radiator core builder machine, put parts together very carefully. Today, radiator making machines help make radiators that work well, last long, and fit many cars.
Key Takeaways
- Radiator making machines help build strong radiators. They shape, put together, and test parts. These machines help keep car engines cool.
- Different machines do special jobs in the process. Some make fins, some put together cores, and some join parts. Others check for leaks to make sure everything works well.
- Automation uses PLC controls and servo motors. This makes work faster and more exact. It also helps stop mistakes when making radiators.
- Aluminum is the best material for radiators. It is lighter and costs less than copper or brass. It also does not rust as easily.
- Radiator fins come in many shapes. These shapes give more surface area and let more air flow through. This helps radiators cool engines better.
- Core builder machines put radiator parts together fast and right. They can make different sizes and styles of radiators.
- Smart manufacturing and green efforts help factories. They use less energy and make less waste. They also recycle better when making radiators.
- New ideas like robotics and new materials help a lot. Advanced controls also make radiators better and faster to produce.
Radiator Making Machine Overview
Radiator making machines help factories build radiators for cars and trucks. These machines shape, put together, and test radiator parts. They make sure each radiator works well and lasts a long time. Radiator making machines are very important in the car industry. They help cars have good cooling systems.
Types of Radiator Making Machines
Factories use many radiator making machines to build radiators. Each machine does a special job. Some machines shape metal parts. Others put the radiator together or check if it works. The table below lists common radiator making machines and what they do:
| Machine Type | Main Role in Production Line |
|---|---|
| Radiator fin machine | Makes cooling fins by rolling and cutting aluminum material. |
| Core builder machine | Assembles radiator cores by placing tubes, fins, and plates together. |
| Plastic tank crimping machine | Joins plastic tanks to aluminum cores using servo motors and robotic arms. |
| Aluminum brazing furnace | Welds radiator core parts together at high temperatures under nitrogen protection. |
| Plastic injection machine | Produces plastic tanks for radiators. |
| Leakage testing machine | Checks radiators for leaks to ensure quality. |
| Manual press machine | Repairs radiators when needed. |
Radiator fin machines are important because they make thin metal fins. These fins help move heat away from the radiator. Core builder machines, like ones from DAG, put all the main parts together. Every machine helps make sure the radiator is made right.
Key Functions in Production
Radiator making machines do many important jobs during production. Each job helps build a strong and safe radiator. The main jobs are:
- Roll form press machines shape radiator panels with fluted profiles.
- Automated decoiler units feed steel coils smoothly for roll forming.
- Spot welding lines up and holds panels before final welding.
- Multi-spot welding makes strong welds along the panels.
- Seam welding joins panel edges for extra strength.
- TIG welding gives careful welds for panel shoulders.
- Panel trimming cuts off extra material for a clean fit.
- Robotic panel stacking puts panels in order for assembly.
- Fixture assembly lines up panels for welding to header pipes.
Radiator fin machines also roll and cut aluminum to make fins. Aluminum pipe expansion machines make tubes inside the radiator bigger. This helps the tubes touch the fins tightly. This step helps the radiator move heat better. Testing machines check for leaks and make sure each radiator works before it leaves the factory.
Note: Modern radiator making machines use robots, sensors, and digital controls. These features help factories make more radiators with fewer mistakes.
Radiator making machines and other equipment work together to build radiators that keep engines cool. Each machine has a clear job in the factory. This teamwork helps factories make the radiators cars need.
Radiator Fin Machine and Fin Forming Machine

Radiator fin machines and fin forming machines are very important in making radiators for cars. These machines shape the fins that help cool engines. A radiator fin machine takes metal strips and turns them into fins with special patterns. The fin forming machine uses rollers and tools to bend the metal without breaking it. This makes the radiator have more surface area, so it can move heat away from the engine faster.
Fin Forming Machine Functions
A fin forming machine does many important jobs when making radiators:
- Makes detailed fin patterns to give more surface area for heat to escape.
- Makes sure every fin is the same size and shape, so the radiator works well.
- Uses rollers and tools to bend metal strips into fins without breaking them.
- Automates the work to make sure it is always correct.
- Helps the radiator work better, so the car stays cool.
The fin forming machine puts raw metal into the system, rolls it into a simple shape, then forms the final fin design, and cuts the fins to the right length. The machine uses a PLC control system to do these steps and check the quality. Most fin forming machines can use both aluminum and copper foils. They only need one person to run them and can connect to automatic feeding systems. The machines keep mistakes small, with a maximum fin size error of ±0.02 mm.
Radiator Fin Rolling Machine Features
A radiator fin rolling machine shapes many kinds of fins for radiators. The machine uses molds to make offset, straight, perforated, louvered, and corrugated fins. These shapes give more surface area and help air move better. The radiator fin rolling machine works with aluminum, copper, and stainless steel. It makes fins quickly and keeps the quality steady. The machine helps make fins that let radiators move heat better. Fin making machines are needed for making heat exchangers. They use different molds to make many fin shapes, which helps radiators work better.
Note: Fins are the main parts that move heat in a radiator. The shapes and designs made by the fin making machine help the radiator cool the engine better.
Fin Types and Applications
Radiator fin machines and fin making machines can make many types of fins. Each fin type has a special job in cooling cars. The table below shows common fin types and how they are used:
| Fin Type | Description | Application in Automotive Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Plate Fins | Flat, rectangular fins; cost-effective; good heat transfer | Used in radiators and condensers for general heat dissipation |
| Louvered Fins | Angled cuts create airflow turbulence to enhance heat transfer | Improve cooling in demanding automotive cooling tasks |
| Wavy Fins | Corrugated surface increases surface area and disrupts airflow | Suitable for compact spaces in radiators and heater cores |
| Pin Fins | Cylindrical pins provide high surface area and heat transfer | Used where maximum cooling efficiency is required |
| Offset Strip Fins | Parallel strips with offsets disrupt airflow and reduce pressure | Balance low air resistance with effective heat transfer |
Tube-fin radiators often use wavy or straight fins to help cool air in cars and machines. Plate-fin radiators, with corrugated or serrated fins, are used in factories and air systems but also help cool cars. Radiator fin machines and fin making machines help make more surface area on radiator tubes. This lets more heat leave the engine coolant and helps cars stay cool.
Fin machine makers design machines that can make all these fin types. The machines help make sure radiators work for many cars and other uses.
Radiator Core Assembly Process
Core Builder Machine
A core assembly machine helps put radiator parts together. The DAG Radiator Core Builder Machine is a popular choice. It uses PLC controls, servo motors, and air-powered systems. These features help the machine work fast and accurately. The machine can lay tubes by hand or by itself. It works with different radiator sizes, like 2-row, 4-row, and 5-row cores. Factories use this machine for many kinds of vehicles.
The DAG machine lets factories order custom designs. It has touch screens that are easy to use. The machine can run by hand, partly by itself, or all by itself. Safety features include two-hand buttons and sensors that find jams. The machine fits both small and big factories. It helps make more radiators faster and better.
| Feature Category | Distinguishing Details |
|---|---|
| Operation Modes | Manual, semiautomatic, and fully automatic options |
| Control Systems | PLC control, touch screens |
| Drive Mechanisms | Servo motors, pneumatic and hydraulic drives |
| Radiator Core Types | 2-row, 4-row, and 5-row core assembly |
| Radiator Size & Fin Specs | Handles various radiator sizes and fin heights |
| Customization | OEM and ODM services |
| Support Services | Technical consulting, installation guidance, training, spare parts, upgrades |
| Production Flexibility | Adjustable settings for different models |
| Safety Features | Two-hand buttons, sensors for jam detection |
| Automation Benefits | Faster production, higher precision, reduced labor, improved quality |
Assembly Steps
The core assembly machine puts header plates, fins, and tubes together. It places each part in the right spot. Here are the steps the machine follows:
- The machine checks the parts before starting.
- It puts tubes and fins in the right order.
- The machine lines up header plates with the tubes and fins.
- It presses the parts together to make the radiator core.
- The machine checks the space between fins and tubes.
- It gets the core ready for brazing.
- The machine moves the core to the next step.
The machine uses jigs to keep parts straight. It uses sensors to find mistakes. The machine can change settings for different radiator types. This lets factories make many kinds of radiators with one machine.
Quality Control
Quality control is very important when making radiator cores. The core assembly machine helps stop mistakes, but factories check quality at many steps.
- Inspectors look at parts before assembly.
- The machine checks the space between fins and tubes.
- Workers watch the brazing process for the right heat and time.
- Inspectors look for problems after brazing, like bent fins or tiny holes.
- The machine puts on tanks and uses sealant to stop leaks.
- Pressure tests fill the radiator with water to check for leaks.
- Inspectors check the radiator’s size, fittings, and how it looks.
- Factories use special tools to find hidden problems.
- Workers fix bent fins before shipping.
- Factories ask customers for feedback to get better.
Common problems are tanks that do not line up, tiny holes, and bent fins. The machine uses jigs and sensors to help stop these problems. If there are problems, workers fix them before shipping. Factories follow rules like ISO 9001:2008 to keep quality high.
Note: Factories check and adjust the core assembly machine often. This helps every radiator stay precise and high quality.
Automation in Radiator Manufacturing
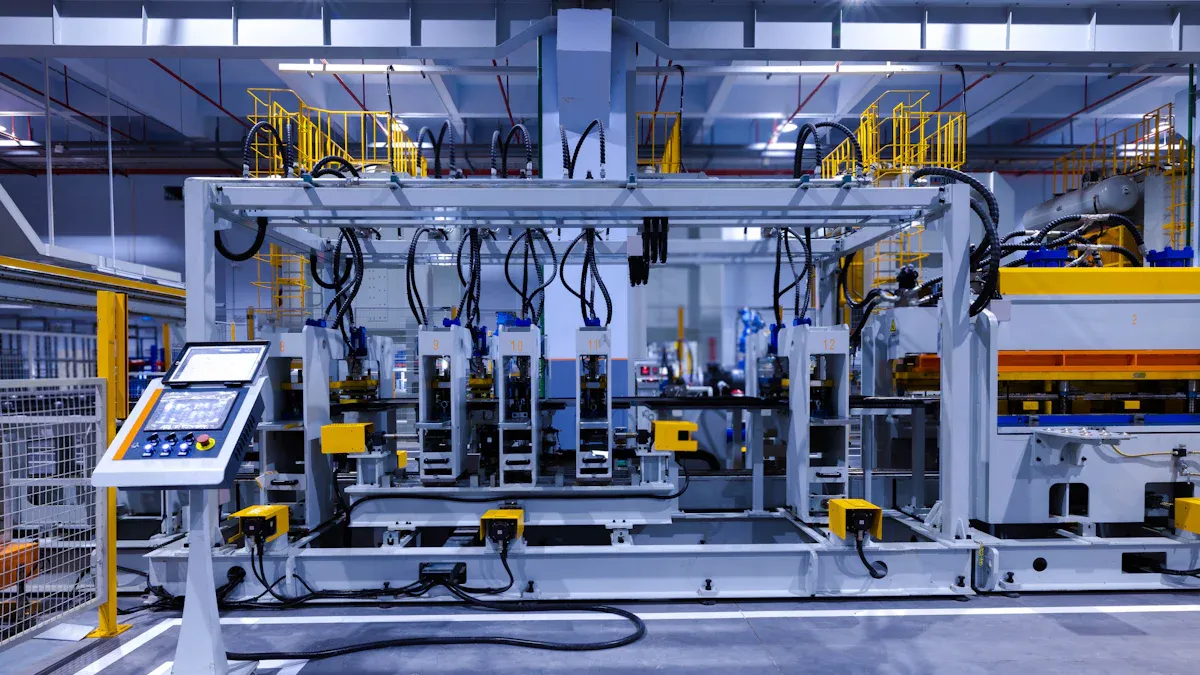

PLC and Servo Control
Modern radiator making machines use PLC systems and servo motors. The PLC is like the machine’s brain. It controls speed and pressure for each fin or tube. Servo motors move metal strips and parts very accurately. This keeps each fin almost the same size, like +0.03mm to -0.01mm. Sensors watch the process and send updates to the PLC. If something goes wrong, the PLC stops the machine fast. This helps stop mistakes and keeps the radiators good.
PLC and servo controls let factories change settings quickly. They can switch fin shapes and sizes with little waiting. The machine saves job settings, so workers do not reset everything. This makes the equipment easy and flexible to use.
Automated Tube and Fin Laying
Automated lines use machines to put tubes and fins in order. The machine picks up each tube and fin and puts them in the right place. Sensors and smart controls check where every part goes. The machine works much faster than people. Some machines can lay up to 600 millimeters each minute. The equipment also checks for mistakes as it works. If it finds a problem, it stops and tells the operator.
- Automated tube and fin laying helps stop mistakes.
- The machine keeps every part in the right spot.
- Sensors and alarms find errors early.
- The process saves time and reduces waste.
Benefits of Automation
Automation gives many good things to radiator making. Machines with PLC and servo controls make work faster and more steady. They help factories make more radiators in less time. The equipment checks each step to keep quality high. This means fewer bad products.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher production rate | Machines work faster than people. |
| Better precision | Servo motors keep parts very close in size. |
| Less waste | Sensors stop the machine if there is a flaw. |
| Flexible equipment | Easy to change for different products. |
| Consistent quality | Automated checks at every step. |
Automated lines help factories use less metal and energy. The machine only uses what it needs. This saves money and helps the environment. Automation also makes it easier for workers to use the machines. They spend less time doing hard work and more time checking quality.
Materials and Technology in Radiator Production
Aluminum and Other Materials
Radiator factories used to make most radiators from copper and brass. Now, many factories use aluminum instead. There are a few reasons for this change:
- Aluminum radiators are much lighter than copper or brass ones. Lighter radiators help cars go faster and use less gas.
- Aluminum is cheaper than copper. This makes radiators cost less to make and buy.
- Aluminum radiators use brazing. Brazing helps heat move better and stops rust.
- Copper radiators use soldering. Soldering does not move heat as well.
- Aluminum makes its own oxide layer to stop rust. Copper needs paint to keep from rusting.
| Aspect | Copper/Brass Radiators | Aluminum Radiators |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavy | 30-40% lighter |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Manufacturing | Soldering | Brazing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Needs paint | Forms oxide layer |
| Cooling Performance | Good, but soldering reduces efficiency | Optimized with fin design |
Aluminum lets factories use better materials in radiator cores. They can make tubes that are bigger and thinner. This helps the radiator cool better and weigh less. Using aluminum helps cars work better and use less fuel.
Brazing and Welding Techniques
Today’s radiator factories use new brazing and welding methods. These ways help make radiators strong and safe.
- No-flux brazing uses a special metal mix. It does not need cleaning after joining parts. This is safer for workers and the planet.
- Laser welding joins thin tubes together. This lets factories make new tube shapes and makes them stronger.
- Brazed joints are stronger than soldered ones. They last longer and can handle more pressure.
- Factories can use the same machines for brazing copper and aluminum radiators.
- Electrophoretic coating adds another layer to stop rust.
Brazing and welding machines work very carefully. They help factories make radiators that last a long time.
Advances in Design
Radiator designs keep getting better. Factories use new ideas to make radiators work well and last longer.
- Aluminum and plastic parts make radiators lighter and cheaper.
- Bigger tubes in aluminum radiators help move heat away faster.
- Multi-core radiators have two or more cores for better cooling.
- Electric fans with sensors control air and save energy.
- Active grille shutters change airflow for better cooling and shape.
- Radiators for electric and hybrid cars help cool batteries and electronics.
Some new radiators use nanofluids to move heat better. Others use smart sensors to watch temperature and change cooling. These new designs help cars stay cool and use less energy. Factories use advanced machines to build these new radiators with great care.
Note: Today’s radiator technology uses better materials, new joining methods, and smart designs. These changes help cars work better and last longer.
Applications and Industry Trends
Automotive Radiators
Radiator making machines are very important in making car parts. These machines help build radiators for cars, trucks, and electric vehicles. Most radiators use aluminum or copper-brass. These materials make radiators lighter and save energy. Factories use special machines to shape, put together, and check each radiator. Many machines now use robots to work faster and make fewer mistakes. This helps factories keep up with more people buying cars everywhere.
Car radiators must keep engines cool. They also need to last a long time and fit many vehicles. New radiator designs use light materials and special fin shapes. These changes help cars use less gas and follow new rules for the environment. Machines can quickly change to make different radiator types. This lets factories build radiators for both gas and electric cars.
| Feature | Automotive Radiators |
|---|---|
| Main Material | Aluminum, copper-brass |
| Focus | Lightweight, energy efficiency, recyclability |
| Application | Cars, trucks, electric and hybrid vehicles |
| Production Method | Automated, high-speed assembly |
Commercial and Industrial Use
Radiator making machines also help make radiators for big machines. These radiators are used in building equipment, farm machines, mining trucks, and power plants. Industrial radiators must be strong and work in tough places. Factories use different materials and designs for these big radiators. The main goal is to make them strong and last a long time.
Industrial radiator machines build bigger and tougher radiators. These radiators cool engines and machines that run for many hours. The machines put together thick tubes and strong fins. They also test each radiator to make sure it works under high pressure and hard jobs. More building and factories mean more need for these strong radiators.
- Commercial radiators cool buses, delivery trucks, and generators.
- Industrial radiators are used in mining, farming, and power plants.
- Machines must change to make different sizes and cooling needs.
Customization and OEM/ODM Services
Factories now get more orders for special radiator designs. Customers want radiators that fit their own vehicles or machines. OEM and ODM services help with these special needs. Companies like DAG have machines that can make many kinds of radiator cores. These machines can change tube size, fin height, and core shape.
Customization helps factories sell to many markets. Machines with smart controls make it easy to switch jobs. Some machines let workers lay tubes by hand or by machine. This makes it easy to fill both small and big orders. More factories want local help and quick service. Companies give on-site help and training to keep machines working well.
Note: The radiator industry now uses new technology, listens to customers, and cares about the environment. Factories use better materials and smart machines to meet what people want.
Future of Radiator Making Machines
Smart Manufacturing
Factories now use smart manufacturing to build radiators. Machines connect to computers and sensors. These systems watch every step as it happens. Workers look at screens to see the data and make fast changes. Robots and servo motors help shape fins and put together cores. Machines use PLC controls to keep each part in the right spot. Some factories use AI and IoT to find problems and fix them quickly. This technology helps factories make more radiators with fewer mistakes. Smart factories also use high-precision cnc manufacturing to cut and shape metal parts. This process makes sure every radiator is the same size and shape. More factories will use radiator core builder machines as these smart tools become popular. Growth will come from new car factories, electric vehicles, and stricter clean air rules.
Sustainability
Radiator factories now try to help the planet. They use new ways to save energy and make less waste. Many companies design radiators so workers can take them apart and recycle the metal. Factories use lightweight materials like aluminum to lower fuel use and emissions. They also work with suppliers who care about the environment. Some companies give longer warranties so people keep radiators longer. Factories run recycling programs and work with recyclers to reuse old radiators. Governments give tax credits and help pay for green research. Many factories use lean manufacturing to save energy and cut waste. They also design parts so they can be fixed and used again.
Factories want to recycle 90% of old radiators in ten years.
Sustainability steps in radiator manufacturing:
- Make radiators easy to take apart and recycle.
- Run recycling programs and work with recyclers.
- Use materials from good sources.
- Give long warranties to cut down on waste.
- Check the whole life of each radiator.
- Use light metals to save fuel.
- Set up closed-loop recycling systems.
- Use lean manufacturing to save energy.
Ongoing Innovations
Radiator making machines keep getting better. Factories now use robots and sensors to work faster and safer. Machines can make many fin types, like straight, wavy, or louvered, in one run. New machines use PLC controls to switch jobs quickly. Some machines use 3D printing to make tricky fin shapes. Factories use new materials, like advanced aluminum alloys and nanotech coatings, to stop rust and help radiators last longer. Machines test each radiator for strength and leaks. These changes help radiators work better in cars, trucks, and electric vehicles. The market will keep growing as more factories want machines that save time, use less energy, and make strong radiators.
Radiator making machines help cars and trucks stay cool. Factories use smart tools to build radiators that last longer. These radiators also work better than before. New materials like aluminum make radiators lighter and stronger. Automation helps factories make more radiators with fewer errors. In the future, radiator makers will use smart technology. They will also use new materials for electric vehicles and other industries.
FAQ
What does a radiator making machine do?
A radiator making machine helps make radiators for cars and trucks. It shapes metal pieces, puts them together, and checks if each radiator is good.
What types of radiators can these machines produce?
These machines can make radiators for cars, trucks, buses, and big machines. They can build many sizes and shapes for different jobs.
What is a radiator core builder machine?
A radiator core builder machine puts the main radiator parts together. It lines up tubes, fins, and plates to make a strong radiator.
What materials do radiator making machines use?
Most machines use aluminum or copper-brass. Aluminum is lighter and costs less. Some machines also use stainless steel for special radiators.
What is the role of automation in radiator manufacturing?
Automation helps machines work faster and more carefully. It lowers mistakes and keeps every radiator the same size and shape.
What are radiator fins, and why are they important?
Radiator fins are thin strips of metal. They help move heat away from the engine. More fins help cool the engine better.
What services do companies like DAG offer?
DAG gives machines for making radiators. They also give technical help, training, and custom machine designs for different needs.
What is the benefit of using PLC control in these machines?
PLC control lets machines follow set programs. It helps change settings fast and keeps the building process steady and safe.