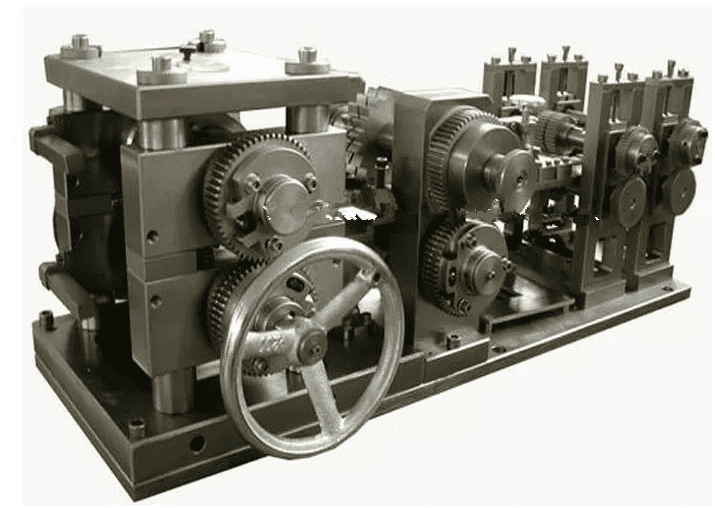
Manufacturers pick the right brazing furnace by looking at their production quantity needs, what materials they use, and what the process requires. A continuous brazing furnace works well for making lots of parts fast. It is good for places like car radiator factories. These places need things done quickly and the same way every time. Batch furnaces are better if you make smaller amounts or change products often. Vacuum furnaces are used when you need very clean air and high quality. They are important for things like airplane and medical parts.
- Continuous belt furnaces are best for making many parts.
- A batch-type furnace is the most common type.
- More people use vacuum aluminum brazing furnaces as electric cars and airplanes become popular.
Picking the right Aluminum Brazing Furnace helps you get good results and do the job right.
Key Takeaways
- Continuous brazing furnaces make many parts fast. They keep quality steady and save energy.
- Batch furnaces are good for small jobs and custom parts. They can change processes easily but use more energy for each part.
- Vacuum furnaces make the cleanest joints with high joint strength. They work best for special metals in aerospace, medical, and electronics.
- Good atmosphere control in the furnace stops oxidation. It makes joints stronger and improves the quality of brazed components.
- Picking the right furnace depends on your production quantity needs, what material you use, part size, and your budget.
- Continuous vacuum furnaces are fast and make clean, strong parts. They save energy and are good for big jobs.
- Batch furnaces let you change processes easily. They can handle big or heavy parts but need more manual work.
- Using a checklist and asking experts helps factories choose the best furnace. This helps them avoid expensive mistakes.
Furnace Types
Continuous Brazing Furnace

Key Features
A continuous brazing furnace moves parts on a conveyor. The parts go through different heating zones. The furnace maintains a steady furnace temperature and atmosphere. Excellent temperature uniformity throughout the heating zones helps achieve high joint strength and clean joints. Nitrogen is used to keep oxygen away from the parts. Most nitrogen goes in near the end of the heated muffle. Some nitrogen flows backward to push out oxygen. Some nitrogen moves forward to stop air from coming in. Mechanical curtains and special nozzles help control the nitrogen. These tools also help use less nitrogen. This setup keeps the air clean and stops oxidation during brazing.
The DAG 700KW Continuous Aluminium Radiator Brazing Furnace is a modern example. It uses resistance heating and has a 10-meter muffle. The furnace can reach a furnace temperature of 650°C. It uses a mesh belt to move parts smoothly. The temperature stays steady. Nitrogen protects the workpieces. The design is good for making many parts fast. Factories can make lots of parts quickly and with the same quality.
Typical Applications
Continuous-belt furnaces are used in places that make many parts. These places include:
- Automotive factories that make radiators, fuel lines, and heat exchangers.
- HVAC companies that need strong, leak-proof joints for heat exchangers.
- Aerospace plants that join turbine blades and fuel systems.
- Medical device makers that need clean, precise joints.
- Electronics factories that make connectors and heat sinks.
A continuous brazing furnace helps these industries make strong, clean joints. The base materials do not melt. The process is fast and saves money. This makes it good for mass production. The DAG 700KW Continuous Aluminium Radiator Brazing Furnace is often used for aluminum radiator brazing. High quality and speed are very important here.
Batch Furnaces
Main Uses
A batch-type furnace heats groups of parts together. Workers load the parts, heat them, and take them out after. This type is good for small jobs or when products change often. A batch-type furnace can handle big or heavy parts. They can also reach different temperatures for each group. They are common in shops that harden gears or treat special alloys.
| Aspect | Batch Furnaces | Continuous Furnaces |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Process materials in groups; workers load by hand | Materials move through at a steady speed; no grouping |
| Complexity | Easier to use and fix | More complex, needs more care |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses more energy per part because of cycles | Saves energy, runs at steady temperature |
| Workload Handling | Needs workers and racks for parts | No racks needed; parts move all the time |
| Temperature Control | Can change temperature for each group | Temperature stays the same for all parts |
| Applications | Good for small jobs, special work, or research | Best for big jobs and making many parts |
Flexibility
Batch furnaces are very flexible. Factories can change the process for each group. This makes it easy to switch products or materials. This is helpful for custom parts or tests. Batch furnaces can do many heat treatments like hardening, annealing, and tempering. They work with many sizes and shapes. They use more energy per part than continuous furnaces. But they let factories change jobs quickly.
Batch Vacuum Furnaces

Process Advantages
Batch vacuum furnaces use a vacuum chamber to remove air and gases. This stops oxidation and keeps parts clean. The vacuum furnace makes strong joints with vacuum brazing. There is no flux left behind. It can join different metals and keeps the base materials safe. A modern vacuum furnace control system allows batch vacuum furnaces to control temperature very well. They can use high gas pressure or oil for cooling. The vacuum helps stop chemical reactions and surface problems. This improves the quality of the final brazed components.
Batch vacuum furnaces are used in aerospace, automotive, tool and die, medical, and electronics. They can work with many types and sizes of parts. The design uses radiant heat and can reach high vacuum levels. This is important for reactive metals and superalloys. The hot zones can be removed and parts can be changed easily. This makes fixing the furnace easier.
Limitations
Batch vacuum furnaces have some limits. To make more parts, factories need more furnaces. This costs more and needs more care. Each cycle lets air and water into the chamber. The system needs strong pumps and high vacuum. The furnace heats and cools for each group. This uses more energy and takes longer. The design must balance insulation and gas flow. This can lower thermal efficiency. Heating and cooling many times can stress furnace parts. This means more repairs. Big loads can cause uneven heat and slow cooling. Batch vacuum furnaces are best for small or medium groups. They are used when quality matters more than speed.
Continuous Vacuum Furnaces

High-Volume Use
Continuous vacuum furnaces are important in today’s factories. These furnaces use a conveyor to move parts through heating zones. The vacuum stays steady and clean inside the furnace. Many factories use these furnaces for big jobs. Car, electronics, and green energy companies use them to make lots of parts fast.
A continuous-belt furnace works without stopping. This lets parts heat up quickly and keeps quality the same. The conveyor moves at one speed, so every part gets equal heat, ensuring consistent performance and quality. Different heating zones help control the temperature at each step. This makes strong and clean joints, which is needed for vacuum hardening and other heat jobs.
Continuous vacuum furnaces are good for making many parts. They run all day, so factories do not stop and start. This means less waiting and more parts made each day. Automation means fewer workers are needed. Workers do not have to load or unload each group of parts. The process stays steady, and mistakes happen less often.
Factories pick continuous vacuum furnaces to keep the vacuum clean. The design stops air or gases from getting inside. This helps stop oxidation and keeps parts clean. The system uses less energy because it does not heat and cool for each group. The continuous-belt processing method does not need racks or baskets, which saves time and energy.
Cost Factors
Continuous vacuum furnaces help factories save money in many ways. The biggest savings come from using less energy. The furnace stays hot and runs all the time, so each part uses less energy than in a batch vacuum furnace. The conveyor and automation also mean fewer workers are needed. This lowers labor costs and makes fewer mistakes.
Multi-chamber continuous vacuum furnaces save even more money. They do not need extra pumps or support tools for each chamber. This lowers the cost to buy and fix equipment. The design keeps the vacuum clean, so there are fewer repairs and less fixing needed.
Continuous-belt furnace systems help control the process better. They let factories manage temperature well and finish jobs faster. Factories can make more parts without buying more furnaces. This makes continuous vacuum furnaces a smart choice for companies that need to make lots of high-quality parts.
Note: Continuous vacuum furnaces work fast, make steady products, and cost less per part. These things make them a good choice for companies that need quick and reliable heat treatment.
Brazing Process Factors
Production Volume
A factory’s production quantity needs matter a lot. If a company needs to make many parts every day, they often pick continuous furnaces. These furnaces move parts through heat zones without stopping. This helps factories make lots of parts fast and keeps things steady. The DAG 700KW Continuous Aluminium Radiator Brazing Furnace is one example. It lets factories make many aluminum brazed components like radiators that have high joint strength and consistent quality.
Batch furnaces are better for small jobs or when products change a lot. Workers put in and take out each group of parts by hand. This gives more control over each group but takes longer. Batch vacuum furnaces also work for this. They let workers change how they process each group and can handle different parts each time.
Big factories are starting to use more continuous vacuum furnaces. These furnaces use vacuum technology to keep the process clean and save energy. They help make lots of parts and lower the cost for each one.
| Production Volume | Recommended Furnace Type | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Low to Medium | Batch Furnace | Handles small groups and allows for flexible processing of many parts. |
| High | Continuous Furnace | Supports high production volumes with steady throughput and efficiency. |
Tip: Factories should pick a furnace that fits how many parts they need to make. If they make a lot, they need a continuous furnace. If they make fewer or different parts, a batch furnace is better.
Material Compatibility
The type of material matters when picking a furnace. Vacuum brazing furnaces are good for special materials like titanium alloys, composites, and special brazing alloys. These materials need clean and strong joints. Aerospace companies use vacuum furnaces to join things like turbine blades and heat exchangers. Medical device makers use them for implants and tools that must be clean and strong.
Vacuum technology helps join different metals together. It keeps the temperature steady and stops oxidation. This is good for parts that need to be strong and not rust. Car factories use vacuum brazing for battery coolers and exhaust coolers. New furnace designs help these furnaces work with more materials.
Batch and continuous furnaces are good for common metals like aluminum and copper. They use steady heat and gas to make strong joints. The DAG 700KW Continuous Aluminium Radiator Brazing Furnace is great for joining aluminum to aluminum or copper to copper. It keeps the heat steady and helps make high-quality parts.
- Vacuum brazing furnaces: Best for special, light, and rust-proof materials.
- Batch and continuous furnaces: Good for regular metals and making lots of parts.
Atmosphere Control
Controlling the air in the furnace is very important. It helps make better joints and better products. Batch furnaces use a closed system with special gas. This keeps the process clean and meets cleanroom rules. Workers can take care of the system and change the gas for each group.
Continuous furnaces use a steady flow of special gas, like nitrogen. This gas keeps parts safe from rust while they heat up. The furnace keeps the heat and gas steady as parts move through. This helps factories make lots of parts and keeps things running well.
Vacuum brazing furnaces use strong vacuums to take out air and gases. This stops rust and helps the brazing alloy flow. The result is a clean and strong joint with no extra chemicals needed. Vacuum processing is important for parts that need to be very strong and pure. It also helps when the parts are tricky or packed close together.
| Furnace Type | Atmosphere Control | Operational Mode | Impact on Product Quality and Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Furnace | Closed, inert atmosphere, cleanroom level | Batch (discrete loads) | Precise control, easy maintenance, good for small and clean jobs |
| Continuous Furnace | Continuous inert gas flow (e.g., nitrogen) | Continuous processing | Needs steady control, supports high productivity and energy efficiency |
| Vacuum Furnace | High vacuum (10^-4 to 10^-5 Torr) | Batch or continuous | Removes gases, prevents oxides, gives clean and strong joints |
Note: Good control of the air in the furnace makes better joints and higher quality products. Factories should pick the furnace that fits their process and material needs.
Process Flexibility
Factories need different levels of flexibility for brazing. Some factories must change their process often. Others make many parts the same way. The furnace type changes how much a factory can adjust its work.
Batch furnaces give the most flexibility. Workers can change the temperature and timing for each group. They can also change the air inside the furnace. This helps when making different products or using new materials. Batch furnaces can handle big or heavy parts. They also allow special heat treatments. Factories can adjust the process for each job. This makes batch furnaces good for custom work or research.
Continuous furnaces are best for making lots of parts. These furnaces keep the temperature steady. Parts move through on a conveyor belt. Operators can change the belt speed and heat zones. But the process stays the same for every part. This setup makes every joint strong and even. Loading is automatic, so there are fewer mistakes. Parts move faster through the furnace. Factories that need many parts with the same quality use this method.
The table below shows how batch and continuous furnaces compare:
| Aspect | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Good for small jobs and low production | Best for making lots of parts |
| Flexibility | Can handle different sizes and heat needs | Less flexible, made for steady and even processing |
| Process Customization | Lets workers change heat for each group | Runs at the same temperature with automatic controls |
| Part Size and Weight | Can process big or heavy parts | Usually made for smaller, same-size parts |
| Operational Mode | Works one group at a time | Runs without stopping |
| Energy Efficiency | Cheaper to buy and fix, but uses more energy | Uses less energy because it stays hot and does not need racks |
| Thermal Control | Can control temperature and air closely | Keeps heat steady with little change |
Vacuum furnaces are also flexible. They are good for parts that need clean air. Operators can set the temperature and pressure for each run. This helps make strong and clean joints in special materials. Vacuum furnaces usually work in groups, so they are slower than continuous furnaces.
Note: Batch furnaces give the most control. Continuous furnaces are fast and make parts the same way. Vacuum furnaces are best when you need clean air and exact heat.
Cost Considerations
Factories must think about both buying and running costs. Each furnace type has different costs.
Batch furnaces cost less to buy. They are simple and easy to fix. Workers can repair them without special tools. But batch furnaces use more energy for each part. They heat up and cool down for every group. They also need more workers to load and unload parts.
Continuous furnaces cost more to buy and set up. They are more complex and need careful controls. Maintenance happens more often and needs skilled workers. But these furnaces use less energy for each part. They stay hot and run all the time. Automation means fewer workers are needed. This helps avoid mistakes.
Vacuum furnaces cost the most to buy and run. They use advanced controls and need regular care. Workers must check for leaks and clean parts often. They also replace seals and other parts. Changing oil in vacuum pumps is important. These steps keep the furnace working well. Even though they cost more, vacuum furnaces are needed for high-quality joints in aerospace and electronics.
The table below compares batch and continuous furnace costs:
| Feature | Batch Furnaces | Continuous Furnaces |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Cheaper because design is simple | Costs more because it is complex |
| Maintenance Costs | Needs less fixing, easier to repair | Needs more fixing, harder to repair |
| Energy Consumption | Uses more energy for each part | Uses less energy for each part |
| Labor Requirements | Needs more workers for loading and unloading | Needs fewer workers, more machines |
| Complexity | Simple design | More complex |
Vacuum furnaces need extra care. Workers must check door seals and look for leaks. They must follow safety steps. Maintenance means cleaning, oiling, and changing old parts. These steps keep the furnace hot and the vacuum strong for each job.
Tip: Factories should pick a furnace that fits their budget and needs. High-quality brazing may cost more at first. But it can make better products and cause fewer problems later.
Pros and Cons
Continuous Brazing Furnace
A continuous brazing furnace lets factories make lots of parts fast. It uses a conveyor belt to move parts through hot zones. Workers can change the belt speed and heat in each zone. This helps make many parts and keeps the process steady.
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Makes lots of parts quickly and keeps quality the same | Needs a lot of money to buy at first |
| Material Compatibility | Works with many alloys like copper, silver, and nickel | Needs parts to fit well and filler metal placed carefully |
| Maintenance | Simple air control means less fixing needed | Can bend or twist parts if not set up right |
| Flexibility | Workers can change belt speed and heat zones | Not as good for small or special jobs |
| Process Challenges | No vacuum needed, so it is easier to use | Parts can get too soft or change shape if not careful |
Factories that make lots of parts every day often pick a continuous brazing furnace. This furnace does not need a vacuum, so it is easier to take care of than a vacuum furnace. Workers must make sure parts fit right and put the filler metal in the correct spot to stop problems.
Batch Furnaces
Batch furnaces heat groups of parts at the same time. Workers put parts in, heat them, and take them out after. This way gives more control over each group.
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Can work with different sizes and types of parts | Slower if you have a big job |
| Process Control | Workers can set different heat for each group | Needs more hands-on work |
| Energy Use (Startup) | Uses less energy for small jobs | Uses more energy for each part if the job is big |
| Maintenance | Simple design, easy to fix | Loses more heat when doors open |
| Automation | Can use some machines to help | Not as automatic as continuous furnaces |
Batch furnaces are good for factories that make small or special orders. Workers can change the process for each group of parts. This furnace uses energy only when running a group, so it saves money for small jobs. For big jobs, it uses more energy for each part because it heats and cools every time.
Batch furnaces give the most control. They are good for shops that change what they make or need to try new ways.
Batch Vacuum Furnaces
Batch vacuum furnaces use a vacuum chamber to take out air and gases. This keeps parts clean and stops rust. These furnaces help make strong and pure joints, which is important for airplane and medical parts.
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Clean Joints | Vacuum takes out air and gases, so parts stay clean | Slower because each group needs to reach vacuum |
| Material Compatibility | Can join special metals and alloys | Costs a lot to buy and keep working |
| Process Control | Workers can set heat and pressure for each group | Needs skilled workers to check for leaks and keep vacuum |
| Flexibility | Can work with different sizes and shapes | Uses more energy for each part than continuous furnaces |
| Product Quality | Makes strong and pure joints with no extra chemicals | Only good for small or medium groups |
Batch vacuum furnaces help factories that need very clean and strong joints. Workers can change the process for each group. These furnaces work best for small or medium jobs where quality is more important than speed. Workers must check the vacuum system often to keep it working well.
Batch vacuum furnaces are important for making parts that must be clean and strong. They cost more to run but give the best results for special jobs.
Continuous Vacuum Furnaces
Continuous vacuum furnaces help factories make lots of parts fast. These furnaces use a conveyor to move parts through hot zones. The vacuum inside stays steady and clean. This keeps the air pure and protects the parts from dirt.
Factories use these furnaces when they need to make many things. The conveyor moves parts at the same speed all the time. Each part gets the same heat. This makes sure every part turns out the same. Car, electronics, and green energy factories often pick this furnace.
The table below shows how batch vacuum furnaces and continuous vacuum furnaces are different:
| Aspect | Batch Vacuum Furnaces | Continuous Vacuum Furnaces |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Good for small or medium jobs | Made for making lots of parts |
| Material Handling | Needs baskets or racks for parts | Uses conveyors to move parts |
| Product Consistency | Heat can change between groups | Same heat for every part |
Continuous vacuum furnaces have some big benefits:
- They can load and heat parts at the same time. This means less waiting and less work for people.
- The vacuum and heat stay steady. This helps every part get the same treatment, so quality stays high.
- Only the parts get hot and cool down, not the whole furnace. This saves energy and makes things go faster.
- Factories can make more parts easily. The design works well with machines, so there are fewer mistakes.
Note: Continuous vacuum furnaces are best for factories that need to make many good parts every day. The steady process and machines help save money and keep quality high.
Choosing a Furnace
Decision Checklist
Picking the right furnace for brazing takes planning. A checklist helps factories choose the best furnace for their needs. Here is a simple list to help with the choice:
- Find out which materials need brazing. See if they react with air or make gases when hot.
- Count how many parts are needed each day. If you need a lot, you may need a continuous furnace.
- Look at the size, shape, and weight of the parts. Some furnaces are better for big or heavy things.
- Set the right temperature and pressure for the job. Some metals need special heat or pressure.
- Pick how to cool the parts. Water or air cooling can change how long the job takes.
- Check if the job must follow any special rules or standards.
- Plan how to load and clean the parts before brazing.
- Decide how smooth and exact the parts must be.
- Write down any extra steps, like cooling fast or testing, after brazing.
- Make sure to include ways to check quality and keep records.
The table below shows what to think about and why it matters:
| Decision Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Component type and geometry | Shapes and sizes change how parts are loaded and heated |
| Productivity requirements | How many parts and how fast the furnace works |
| Load size | Big or heavy loads need the right furnace |
| Temperature and pressure | The furnace must reach the right settings |
| Cooling medium | Gas or oil cooling changes how fast parts cool |
| Compliance and specifications | Some jobs need special features for rules |
Tip: Factories should use this checklist to help pick the best furnace for their brazing jobs.
Matching Needs to Furnace Type
Factories need to match their brazing jobs to the right furnace. Continuous-belt furnaces are good for making lots of parts fast. They keep the work steady and quick. Batch vacuum furnaces are better for small jobs or special metals that react with air. These furnaces keep metals safe from rust.
Factories should also look at the shape and size of their parts. Big or tricky parts may need batch furnaces. If the job must follow strict rules, vacuum furnaces are often needed. Factories should think about all costs, not just the price to buy the furnace. Energy, repairs, and help from experts are important too.
Talking to furnace makers or experts can help avoid mistakes. Experts can check the warranty, support, and special needs for the job. They can also help plan for changes in what the factory makes later. Factories should ask about service, spare parts, and training for workers.
Note: Asking experts for help makes it easier to pick the right furnace and avoid costly mistakes.
Picking the best brazing furnace depends on what you make, what materials you use, and what the job needs. Some important things from new case studies are:
- Keeping the right heat and air in the furnace makes strong, clean joints.
- Special furnace designs and machines help work faster and make better parts.
- Continuous furnaces, like the DAG 700KW, are good for making lots of aluminum parts. They work well and save energy.
Using a checklist of good and bad points helps factories pick the right furnace. Talking to experts or trusted companies helps keep the choice safe and saves money.
FAQ
What is the main difference between batch and continuous brazing furnaces?
Batch furnaces heat parts in groups at one time. Continuous furnaces use a conveyor to move parts through hot zones. Continuous furnaces are best when factories need to make many parts quickly.
When should a factory choose a vacuum brazing furnace?
A factory should pick a vacuum brazing furnace for clean and strong joints. These furnaces stop oxidation and work well with special metals.
Can the DAG 700KW Continuous Aluminium Radiator Brazing Furnace handle different part sizes?
The DAG 700KW furnace can work with many part sizes. Factories can change the belt speed and adjust the size to fit what they need.
How does atmosphere control affect brazing quality?
Atmosphere control keeps oxygen away from the parts. This stops oxidation and helps make strong, clean joints. Good control means better product quality.
What maintenance does a continuous brazing furnace need?
Operators should check the mesh belt, heating parts, and seals often. Cleaning and checking the furnace helps it run well and last longer.
Is a continuous furnace more energy efficient than a batch furnace?
Yes. Continuous furnaces use less energy for each part. They stay hot and do not stop, so they save energy and lower costs.
How can a factory decide which furnace type to buy?
Factories should think about how many parts they make, what materials they use, part size, and their budget. They can use a checklist or ask furnace experts for help.